| Active with remarks |
|---|
| This application needs additional settings. Please follow the documentation below to create your own connectionUnique, active service acces point to a network. There are different types of connections (API key, Oauth…). More. |
The Coveo modulesThe module is an application or tool within the Boost.space system. The entire system is built on this concept of modularity. (module - Contacts) More allow you to perform various searches and updates to itemsItems are rows in records (order/request/invoice/purchase...) in your Coveo account.
Prerequisites
-
A Coveo account
In order to use Coveo with Boost.spaceCentralization and synchronization platform, where you can organize and manage your data. More IntegratorPart of the Boost.space system, where you can create your connections and automate your processes. More, you must have a Coveo account. If you do not have one, you can create a Coveo account at coveo.com.
![[Note]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
The moduleThe module is an application or tool within the Boost.space system. The entire system is built on this concept of modularity. (module - Contacts) More dialog fields that are displayed in bold (in the Boost.space Integrator scenarioA specific connection between applications in which data can be transferred. Two types of scenarios: active/inactive. More, not in this documentation article) are mandatory! |
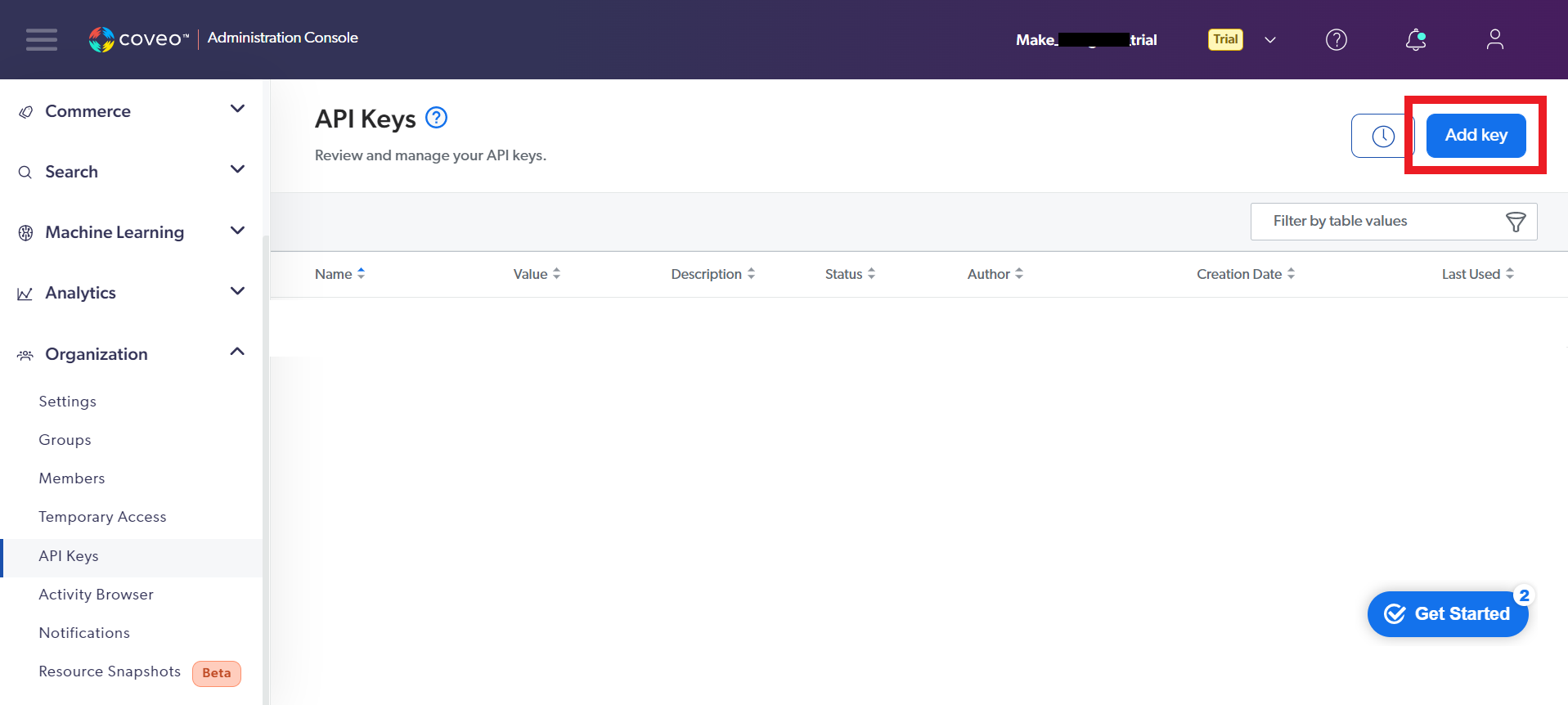
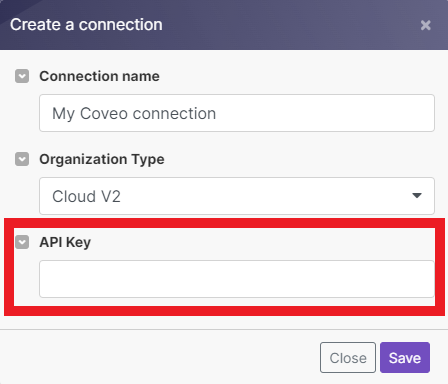
To connect your Coveo account to Boost.space Integrator you must obtain an API Key.
-
Log in to your Coveo account.
-
Under Organization in the left-hand menu, click API Keys.
-
Click Add key.
-
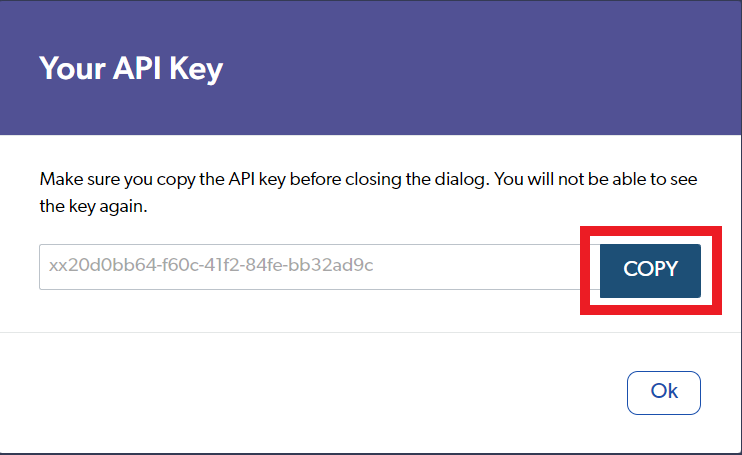
Configure your API key and make sure to provide privilege and access information.
-
Click Copy to copy your API key to your clipboard. You will not be able to see the key again after this.
-
In Boost.space Integrator, choose the Coveo module you want to use. Next to Connection, click Add.
-
Choose a name for your connection and select the Organization type. Enter your API Key.
You have now established the connection.
Retrieves a list of query suggestions.
|
Connection |
|
|
Query |
Enter your query. |
|
Enable Word Completion |
Select whether to attempt to complete the last word of the current basic query expression and boost the ranking score of the resulting expression so that it is returned as the first query suggestion. |
|
Locale |
Enter the locale of the current userCan use the system on a limited basis based on the rights assigned by the admin. More. Must comply with IETF’s BCP 47 definition. For example: |
|
Search Hub |
Enter the search hub. The Search Hub is the first level of origin, typically the identifier of the graphical search interface from which the request originates. |
|
Pipeline |
Enter the name of the query pipeline to use. If a query does not contain the pipeline parameter, the first query pipeline whose conditions are met by the request is used (query pipelines without conditions are not evaluated). |
|
Timezone |
Select the timezone. If not specified, the default time zone of the server hosting the index is used. |
|
Limit |
Set the maximum number of suggestions Boost.space Integrator returns during one scenario execution cycleA cycle is the operation and commit/rollback phases of scenario execution. A scenario may have one or more cycles (one is the default).. |
Performs a simple query.
|
Connection |
||||
|
Basic Query Expression |
Enter your basic query expression. You can also use the built-in query suggestion tool. |
|||
|
Advanced Query Expression |
Enter an advanced query expression. For example: |
|||
|
Search Hub |
Enter the search hub. |
|||
|
Sort Criteria |
Select how you want to sort the query results. This only works when combining either two or more field criteria or a single date criteria with one or more field criteria.
|
|||
|
Limit |
Set the maximum number of results Boost.space Integrator returns during one scenario execution cycle. |
Performs an advanced query.
|
Connection |
||||
|
Basic Query Expression |
Enter your basic query expression. You can also use the built-in query suggestion tool and refer to the Perform a Simple Query module documentation. |
|||
|
Enable Did You Mean |
Select whether to enable the Did You Mean feature of the index.
|
|||
|
Partial Match |
Select whether to convert a basic expression containing at least If you do not set this parameter to |
|||
|
Enable Wildcards |
Select whether to enable the wildcards feature of the index. See Using Wildcards in Queries. |
|||
|
Enable Query Syntax |
Select whether to interpret advanced Coveo Cloud query syntax as such in the basic query expression. |
|||
|
Enable ML Did You Mean |
Select whether to enable the Coveo ML query suggestions Did You Mean feature. |
|||
|
Advanced Query Expression |
Enter an advanced query expression. For example: |
|||
|
Constant Query Expression |
Enter a constant query expression. For example: The constant query expression, typically populated with expressions that must apply to all queries sent from a specific search interface (e.g., from a specific tab). Once evaluated, the result sets of those expressions are kept in a special cache.
|
|||
|
Disjunction Query Expression |
Enter a disjunction query expression. For example: The disjunction query expression, typically populated by Coveo ML automatic relevance tuning models to ensure that relevant items are included in the query results. The resulting query expression is |
|||
|
Large Query Expression |
Enter a large query expression. For example: The large query expression, typically populated with a case description, long textual query, or any other form of text that can help refine a query. |
|||
|
Large Query Partial Match Max Keywords |
Enter the maximum number of keywords from the large query expression that will be included in the partial match expression. |
|||
|
Large Query Partial Match Keywords |
Enter the minimum number of keywords that need to be present in the large query expression to convert it to a partial match expression. |
|||
|
Large Query Partial Match Threshold |
Enter a value indicating the minimum number of partial match expression keywords an item must contain to match the large query expression in case the Coveo ML Intelligent Term Detection (ITD) feature cannot extract relevant keywords from the large query expression. For example: |
|||
|
Excerpt Length |
Enter the maximum length of result excerpts (in number of characters). |
|||
|
Retrieve First Sentences |
Select whether to include the first sentences of textual items in the query results. |
|||
|
Fields to Include |
Select the fields to include with each item in the query results. If specified, no other fields will be included. |
|||
|
Fields to Exclude |
Select the fields to exclude from the query results. All other fields will be included with each item in the query result. |
|||
|
Group By |
Select the Group By operationsAn operation is a task performed by module. More to perform on the query results, typically to extract facets. |
|||
|
Facets |
Select the facet operations to perform on the query results. |
|||
|
Facet Options |
Select the global configuration options that apply to all facet requests performed along with the query. |
|||
|
Category Facets |
Select any data to easily query a hierarchical field using a path of hierarchical values. |
|||
|
Sort Criteria |
Select the criteria to use for sorting the query results.
|
|||
|
Ranking FunctionsFunctions you can use in Boost.space Integrator - create, update, delete, get, search. |
Select the array of ranking functions to execute on each query result item. The result of a ranking functionFunctions you can use in Boost.space Integrator - create, update, delete, get, search. is added to the result score, which can affect sorting. |
|||
|
Query Functions |
Select the array of query functions to execute on each query result item. The result of a query function is stored in a temporary, dynamic field created at query time. |
|||
|
Enable Duplicate Filtering |
Select whether to filter out duplicates, so that items resembling one another only appear once in the query results.
|
|||
|
Filter Field |
Select the |
|||
|
Parent Field |
Select the |
|||
|
Child Field |
Select the |
|||
|
Filter Field |
Select the |
|||
|
Search By ID |
Select whether the |
|||
|
Syntax |
Enter the name of the query syntax to apply when interpreting the basic query expression. |
|||
|
Summary Length |
Enter the length of the automatically generated item summary. The index generates a result item summary independently from the query, as opposed to a result item excerpt, which is generated based on query keywords. |
|||
|
Static Query |
Select whether to execute this query in a way that does not count against the allowed number of queries per month of a Coveo Cloud organization (QPM), but may produce cached/outdated query results. |
|||
|
User Actions |
Enter the parameters allowing user actions to be retrieved in query results. For example: |
|||
|
Dictionary Field Context |
Add a key-value store where each pair corresponds to the name of a dictionary field to query, along with the key to target within that field. |
|||
|
Pipeline |
Enter the name of the query pipeline to use for this request (bypassing its conditions, if it has any). |
|||
|
Maximum Age |
Enter the maximum age of cached results, in milliseconds.
|
|||
|
Search Hub |
Enter the search hub. The Search Hub is the first level of origin, typically the identifier of the graphical search interface from which the request originates. |
|||
|
Tab |
Enter the tab. The Tab is the second level of origin of the request, typically the identifier of the selected tab in the graphical search interface from which the request originates. |
|||
|
Referrer |
Enter the referrer. The Referrer is the third level of origin of the request, typically the URL of the page that linked to the search interface from which the request originates (e.g., in JavaScript, this would correspond to the |
|||
|
Context |
Enter the custom context information to send along with the request.
|
|||
|
Actions HistoryBoost.space Integrator maintains a history of your scenario and records: The date that scenario execution started Status (success, warning, or error) Execution duration Number of operations spent during the scenario run Size of transferred data Link to detailed information, where you can inspect all data in that particular execution received and how the data was processed You can view this... |
Select the query and page view actions previously made by the current user. |
|||
|
Recommendation |
Enter the identifier of the recommendation interface from which the request originates. |
|||
|
Locale |
Enter the locale of the current user. Must comply with IETF’s BCP 47 definition. For example: |
|||
|
Timezone |
Enter the time zone to correctly interpret dates in the query expression and result items. For example: |
|||
|
Index TokenThe API token is a multi-digit code that allows a user to authenticate with cloud applications. More |
Enter the encoded identifier of the index mirror to forward the request to. |
|||
|
Visitor ID |
Enter a GUID representing the current user, who can be authenticated or anonymous. This GUID is normally generated by the usage analytics service and stored in a non-expiring browser cookie. |
|||
|
ML Parameters |
Configure the map of options to pass to the Coveo ML models associated with the request’s target query pipeline. |
|||
|
Index Type |
Enter the type of index against which to execute the query. Must correspond to an index that has been configured for the target Coveo Cloud organization. |
|||
|
Index |
Enter the identifier of the index mirror to forward the request to. |
|||
|
Logical Index |
Enter the identifier for a logical group of indexes that have been configured to include documents form the same sources. |
|||
|
Maximum Timeout Ms |
Enter the maximum number of milliseconds to allow the request to last before timing out. |
|||
|
Analytics |
Configure the contextual information about the user performing the request and the request itself. See Analytics Request Parameters. |
|||
|
Limit |
Set the maximum number of results Boost.space Integrator returns during one scenario execution cycle. |
For more information, see the Coveo Perform a Query documentation.
Adds an item to a push source by the source ID or updates an item if it exists.
|
Connection |
||||
|
Organization ID |
Select the ID of the target Coveo Cloud V2 organization associated with the item. |
|||
|
Push Source ID |
Select or enter the ID of the target push source. See Creating a Push Source. |
|||
|
Document ID |
Enter the ID of the item. Must be the item URI. For example: |
|||
|
Upload Type |
Select how you want to upload the item. Raw Data: The raw textual item data. Compressed Binary Data: The encoded item data. File Container: The file container where the compressed or uncompressed, binary or non-binary item data was previously uploaded. |
|||
|
File Extension |
Enter the file extension of the item data you are pushing. Value must include a preceding
|
|||
|
Parent ID |
Enter the URI of the parent item. For example: |
|||
|
Permissions |
Set the permission parameters for your item. |
For more information, see the Coveo Push API documentation.
Removes an item to a push source and optionally its children by the document ID.
|
Connection |
|
|
Organization ID |
Select the ID of the target Coveo Cloud V2 organization associated with the item. |
|
Push Source ID |
Select or enter the ID of the target push source. See Creating a Push Source. |
|
Document ID |
Enter the ID of the item. Must be the item URI. For example: |
|
Delete Children |
Select whether to also delete the children of the item. |
For more information, see the Coveo Push API documentation.
Performs an arbitrary authorized API Call.
|
Connection |
||||
|
URL |
Enter a path relative to
|
|||
|
Method |
Select the HTTP method you want to use:
|
|||
|
Headers |
Enter the desired request headers. You don’t have to add authorization headers; we already did that for you. |
|||
|
Query String |
Enter the request query string. |
|||
|
Body |
Enter the body content for your API call. |
The following API call returns all the campaigns from your Coveo account:
URL: organizations
Method: GET
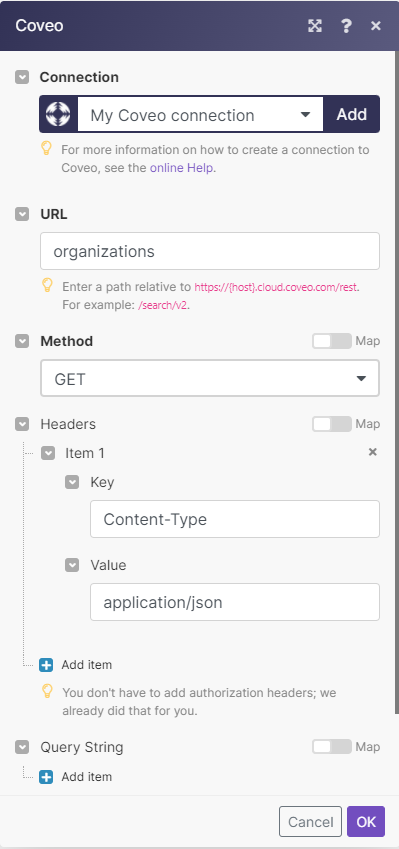
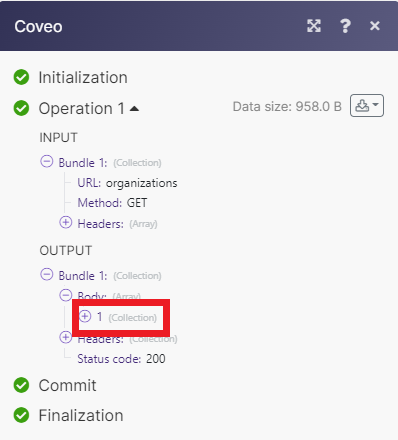
Matches of the search can be found in the module’s Output under BundleA bundle is a chunk of data and the basic unit for use with modules. A bundle consists of items, similar to how a bag may contain separate, individual items. More > Body. Our example returned 1 organization:


![[Tip]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/tip.png)