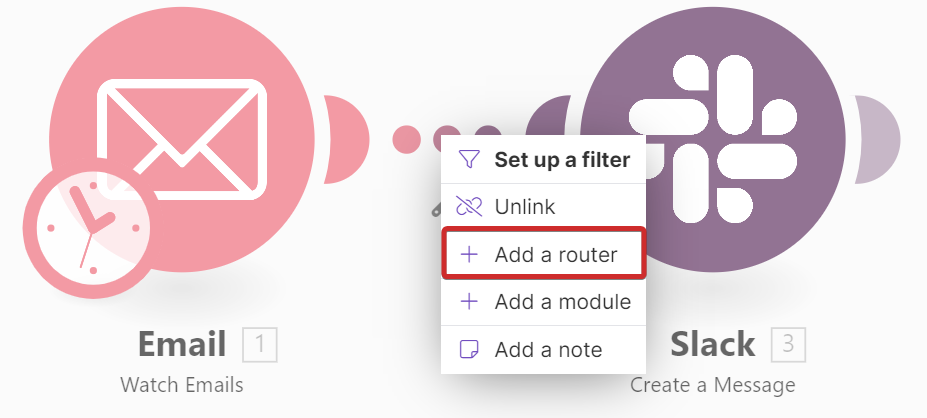
A routerA router allows you to add new routes to a scenario so you can branch your flow into several routes and process the data within each route differently. More allows you to branch the scenarioA specific connection between applications in which data can be transferred. Two types of scenarios: active/inactive. More flow into several chains of modulesThe module is an application or tool within the Boost.space system. The entire system is built on this concept of modularity. (module - Contacts) More. Each route processes the data differently according to the condition you set. Filters help you to determine conditions via different operators such as less than, greater than, and so on.
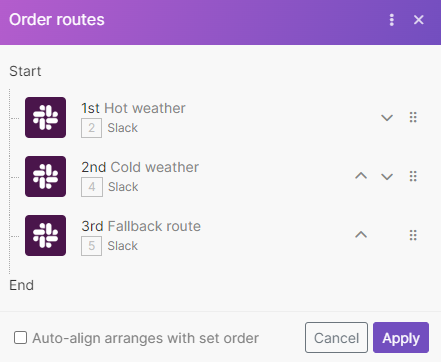
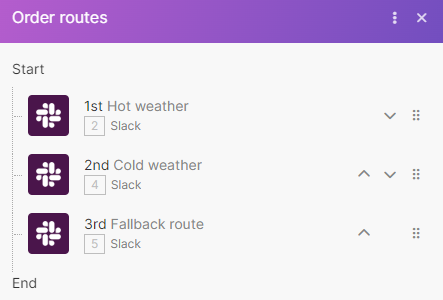
Order routes in the sequence you want and set up a fallback route that will process data that doesn’t fit other routes.
![[Tip]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/tip.png) |
Tip |
|---|---|
|
See our scenario templateTemplates are predefined scenarios that you can expand and customize to create new scenarios. You can then share these with friends and colleagues. More for the Controlled distribution of data flow. |
You can add a router in two different ways:
You can set the order of routes in which Boost.spaceCentralization and synchronization platform, where you can organize and manage your data. More IntegratorPart of the Boost.space system, where you can create your connections and automate your processes. More processes them in the scenario.
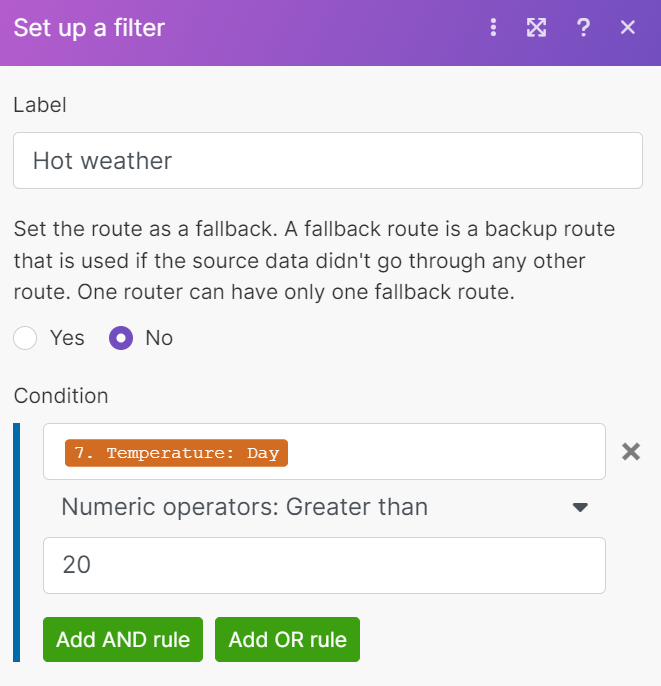
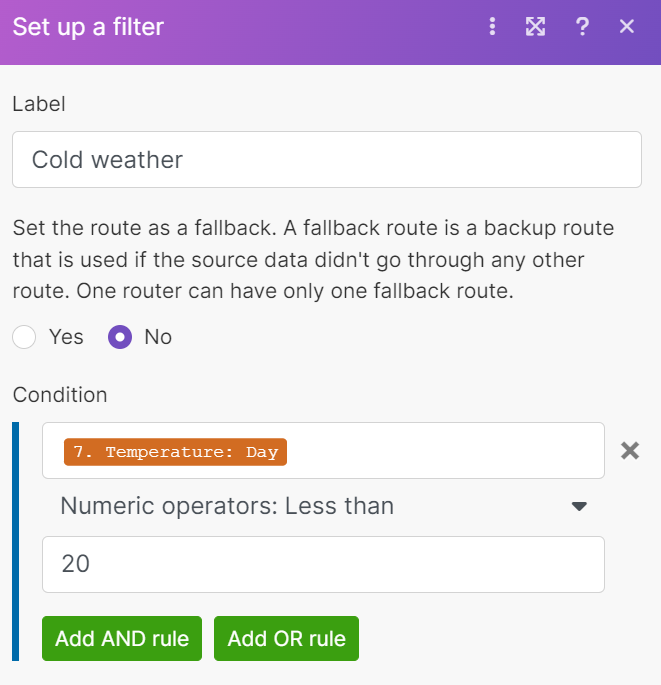
This example shows the router that determines which hint to send you on Slack according to tomorrow’s weather.
-
Click the router that contains the routes you want to order.
-
Right-click and select Order routes. A window appears.
-
Click arrows and move routes according to your needs.
![[Note]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/note.png)
Note The fallback route always runs last, no matter which position it takes in the Order routes window.
-
Optional. Select Auto-align arranges with set order to visually arrange modules on the scenario canvas according to the set order.
-
Click Apply.
![[Note]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
Routes are processed sequentially, not in parallel. Boost.space Integrator won’t process the second route unless it finishes processing the first one. |
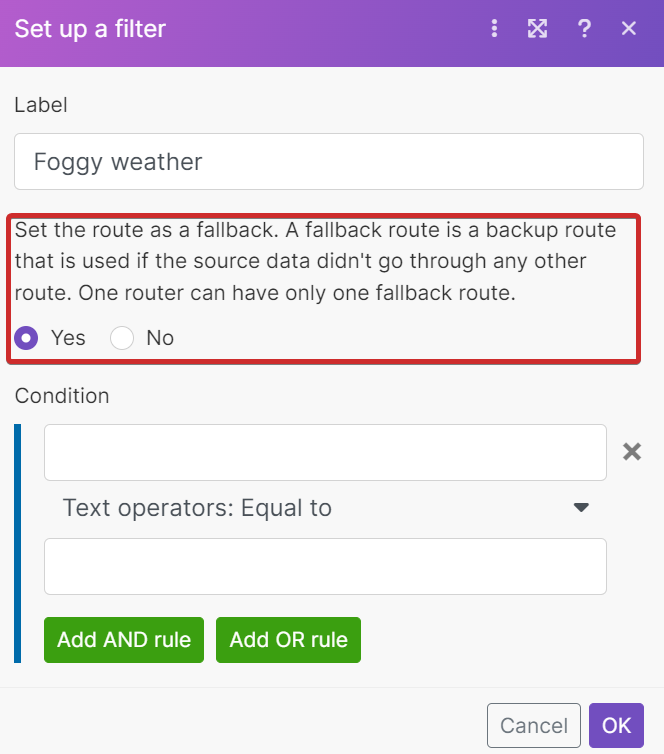
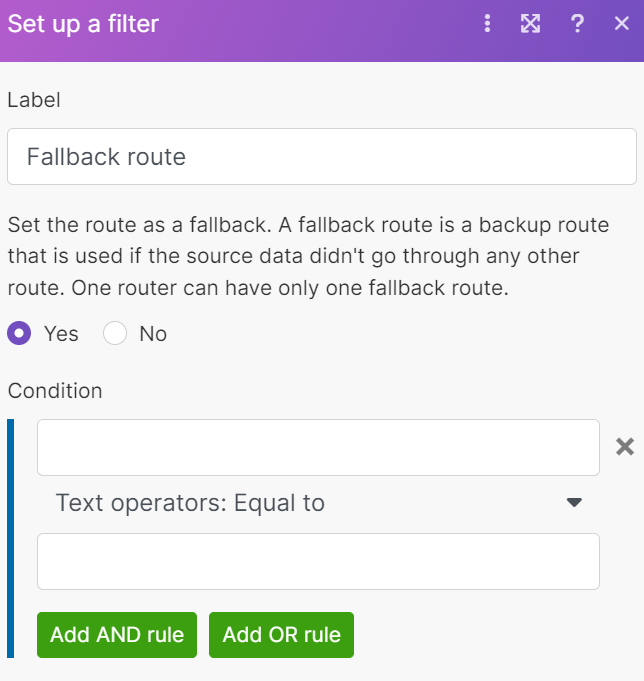
A fallback route processes data that doesn’t fit the condition of all other routes. You can mark a route as a fallback if you want it to be executed last.
![[Note]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
You can set up a filter for a fallback route same as for other routes. |
To set up a fallback route, follow the steps:
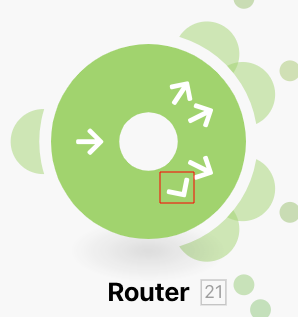
You can recognize the fallback route by the special arrow icon on the router module:
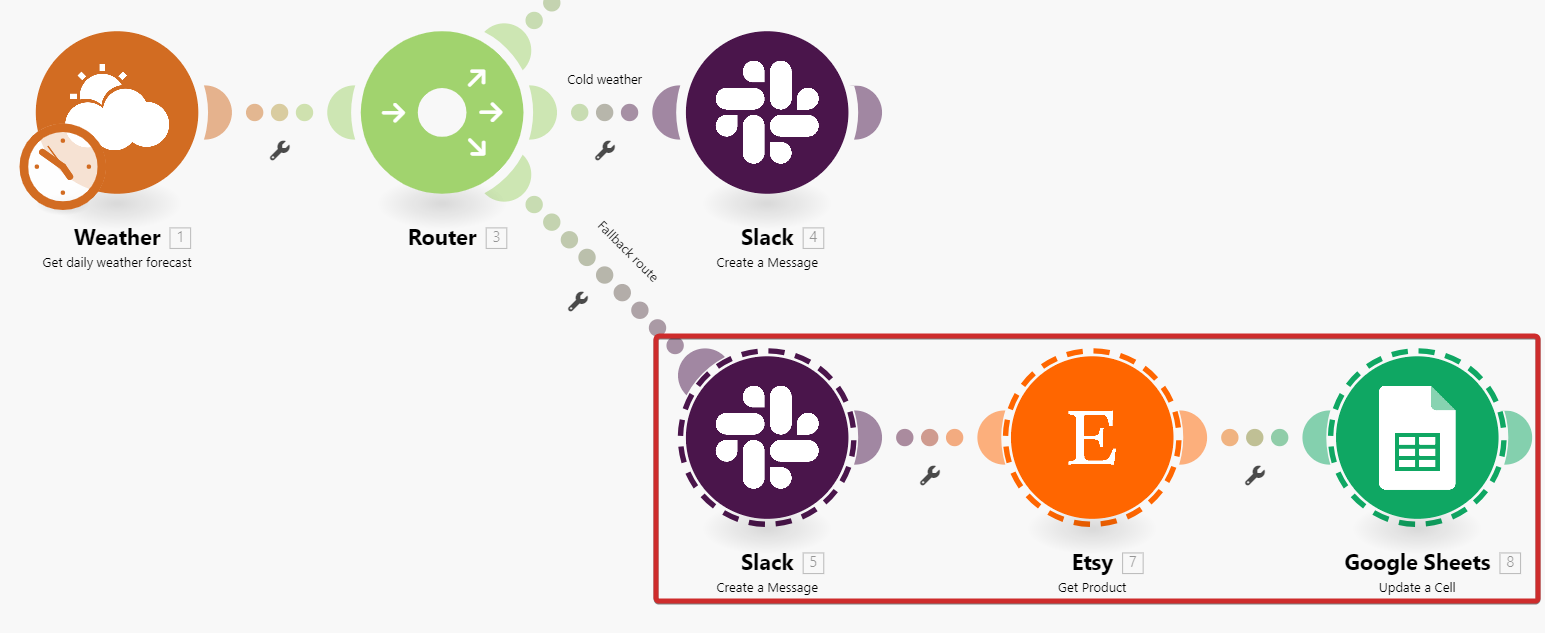
You can manage all modules in the branch at once.
Click the route menu, then click Select whole branch. It selects all the following modules.
You can copy or delete all selected modules at once.
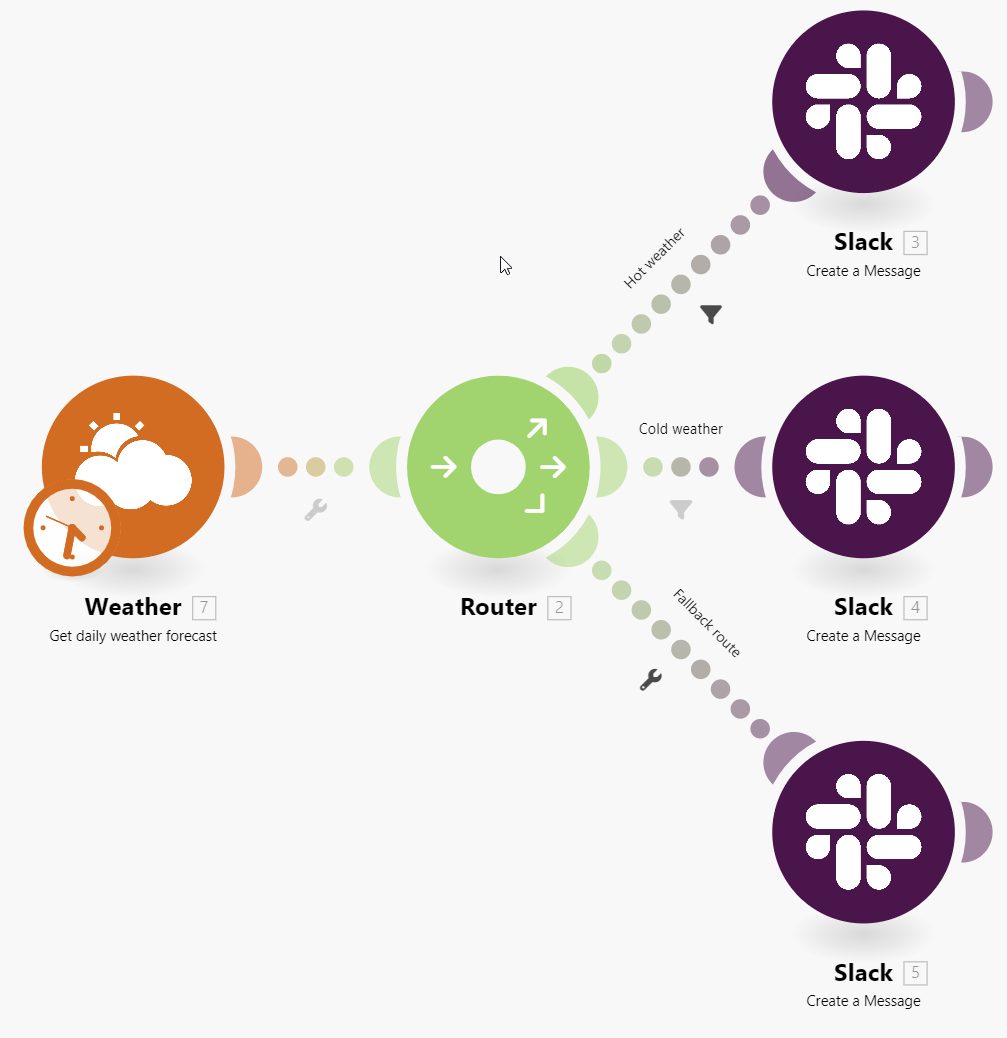
Example 1. Example of a router with a fallback route
You need to receive a message on Slack depending on tomorrow’s weather:
-
if the weather is hot, the message is
wear shorts. -
if the weather is cold, the message is
wear a jacket. -
if the weather is neither hot nor cold, the message is
better stay at home.
The scenario looks like that:
The scenario flow is:
-
The Weather module gets data about tomorrow’s weather.
-
Data goes to the router that processes routes in the determined order: