- Google Sheets
- Connect Modules Using the Google Account Sign In
- Connecting Instant Triggers (Perform a Function, Watch Changes) using the Boost.space Integrator Google Sheets Add-on
- Did you know?
- Triggers
- Actions
- Add a Row
- Update a Row
- Clear a Row
- Delete a Row
- Get a Cell
- Update a Cell
- Clear a Cell
- Add a Sheet
- Create a Spreadsheet
- Perform a Function - Responder
- Delete a Sheet
- Make an API Call
- Example of Use - Get Spreadsheet
- Create a Spreadsheet from a Template
- Copy a Sheet
- Clear Values from a Range
- Add a Conditional Format Rule
- Delete a Conditional Format Rule
- Searches
- Usage Limits
- Tips & Tricks
| Active with remarks |
|---|
| This application needs additional settings. Please follow the documentation below to create your own connectionUnique, active service acces point to a network. There are different types of connections (API key, Oauth…). More. |
With Google Sheets modulesThe module is an application or tool within the Boost.space system. The entire system is built on this concept of modularity. (module - Contacts) More in Boost.spaceCentralization and synchronization platform, where you can organize and manage your data. More IntegratorPart of the Boost.space system, where you can create your connections and automate your processes. More, you can manage rows, cells, sheets, spreadsheets, values, and conditional formats in your Google Sheets account.
To use Google Sheets with Boost.space Integrator, you must have a Google account. If you do not have one, you can create one at accounts.google.com. To use instant triggerEvery scenario has a trigger, an event that starts your scenario. A scenario must have a trigger. There can only be one trigger for each scenario. When you create a new scenario, the first module you choose is your trigger for that scenario. Create a trigger by clicking on the empty module of a newly created scenario or moving the... modules, you must have the Boost.space Integrator Google Sheets extension.
Refer to the Google Sheets API documentation for a list of available endpoints.
![[Note]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
Boost.space Integrator‘s use and transfer of information received from Google APIs to any other app will adhere to Google API Services User Data Policy. |
To connect Google Sheets to Boost.space Integrator, you must first connect your Google account.
-
Log in to your Boost.space Integrator account, add a Google Sheets moduleThe module is an application or tool within the Boost.space system. The entire system is built on this concept of modularity. (module - Contacts) More to your scenarioA specific connection between applications in which data can be transferred. Two types of scenarios: active/inactive. More, and click Create a connection.
-
Optional: In the Connection name field, enter a name for the connection.
-
Click the Sign in with Google button and select your Google account.
-
Review the access information and click Allow.
You have successfully established the connection. You can now edit your scenario and add more Google Sheets modules. If your connection requires reauthorization at any point, follow the connection renewal steps here.
Connecting Instant TriggersEvery scenario has a trigger, an event that starts your scenario. A scenario must have a trigger. There can only be one trigger for each scenario. When you create a new scenario, the first module you choose is your trigger for that scenario. Create a trigger by clicking on the empty module of a newly created scenario or moving the... (Perform a Function, Watch Changes) using the Boost.space Integrator Google Sheets Add-on
In order to use instant triggers, you must install the Boost.space Integrator add-on in your spreadsheet and establish a connection between the Boost.space Integrator module and Google Sheets.
![[Note]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
This add-on works only if you open the Google spreadsheet in a browser and make changes there. It will not work when the spreadsheet is filled by Google Forms or other tools. |
-
Open the spreadsheet where you want to install the extension.
-
Go to Extensions > Add-ons > Get add-ons
-
Search for the Boost.space Integrator add-on.
-
Click on +Free to install the Boost.space Integrator add-on.
-
Click Allow to grant access rights.
-
You have now installed the Boost.space Integrator add-on.
-
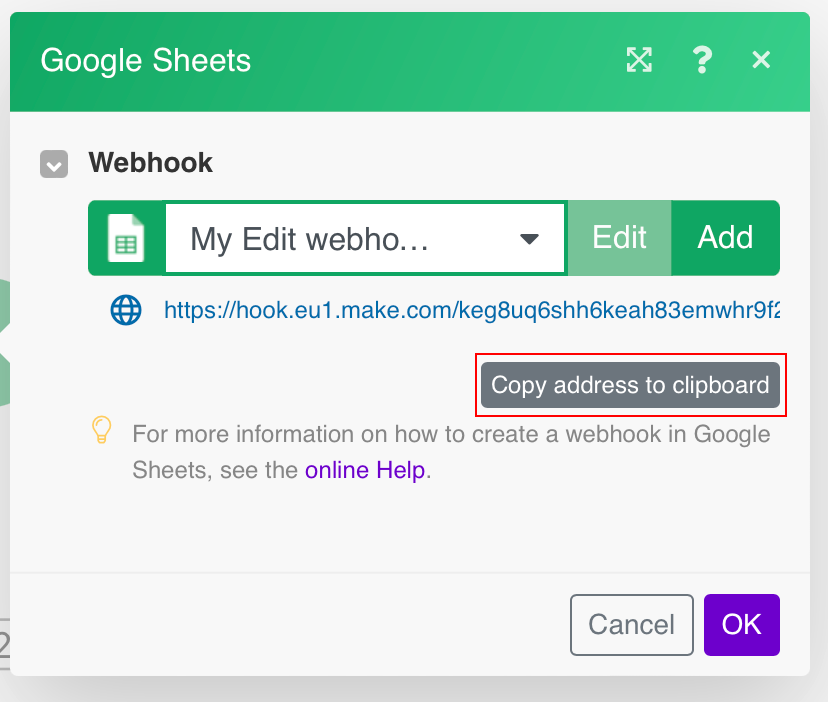
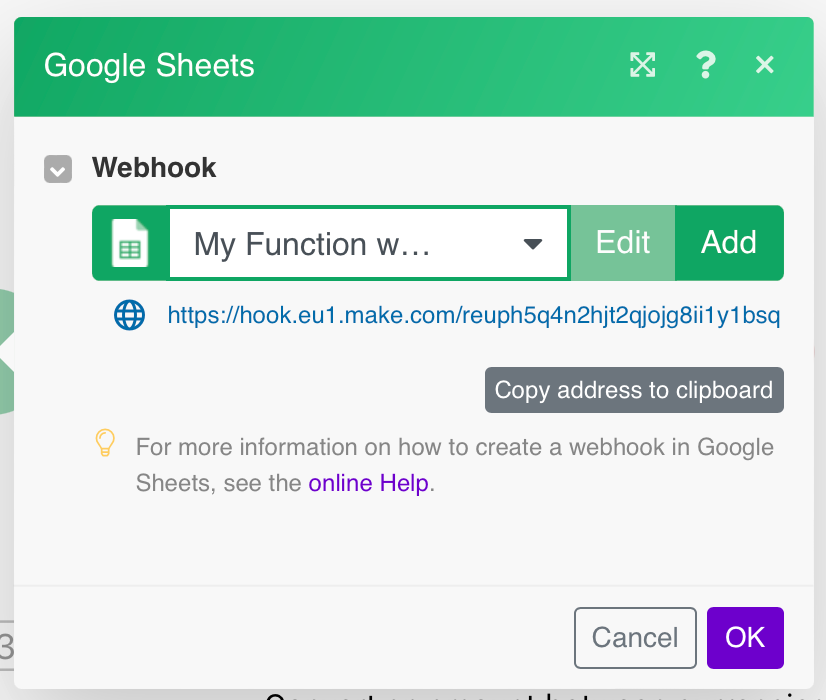
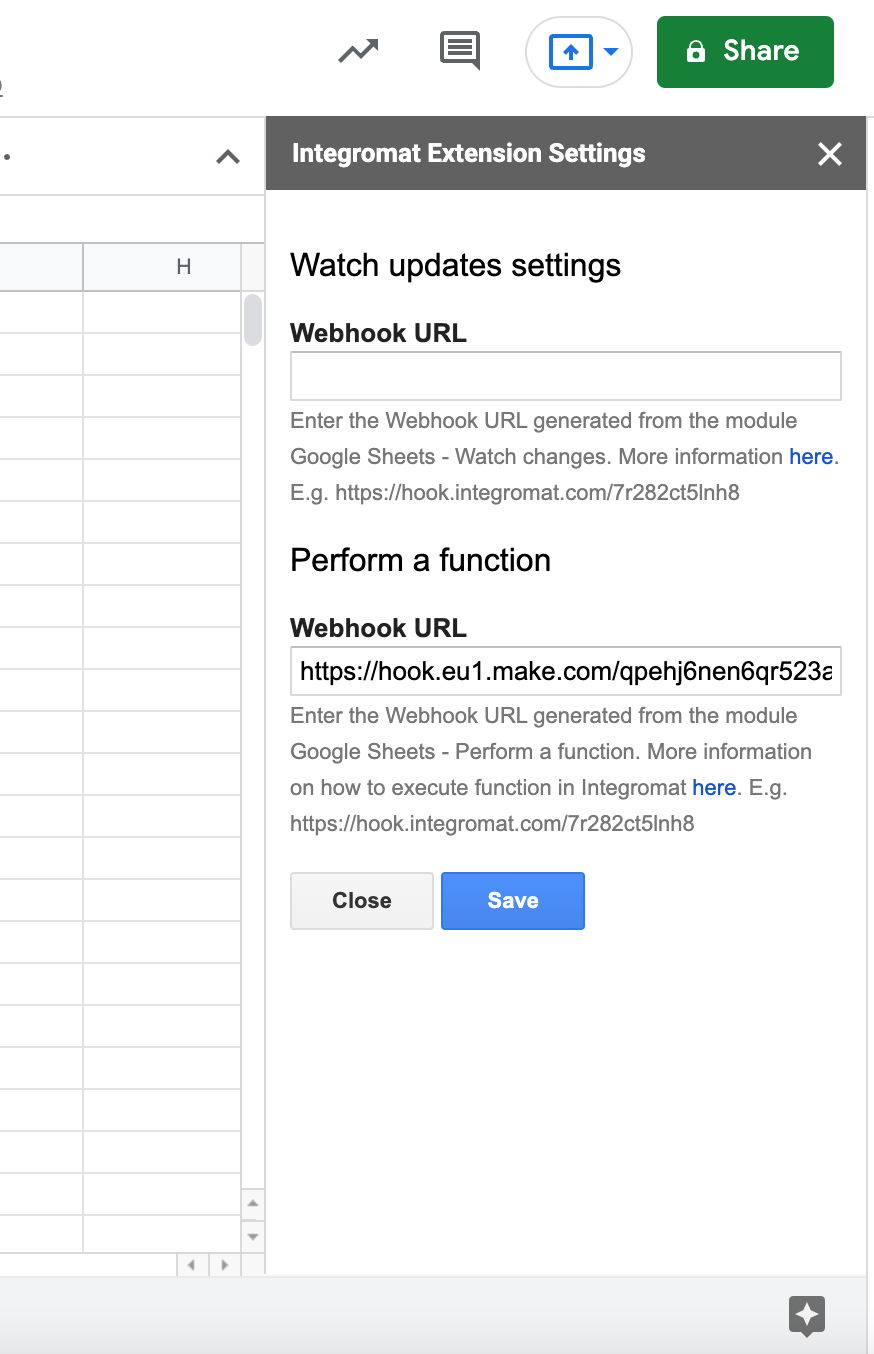
Copy the provided webhookA webhook is a way for an app to send real-time information to a specific URL in response to certain events or triggers. address to the clipboard and click OK.
-
Open your spreadsheet.
-
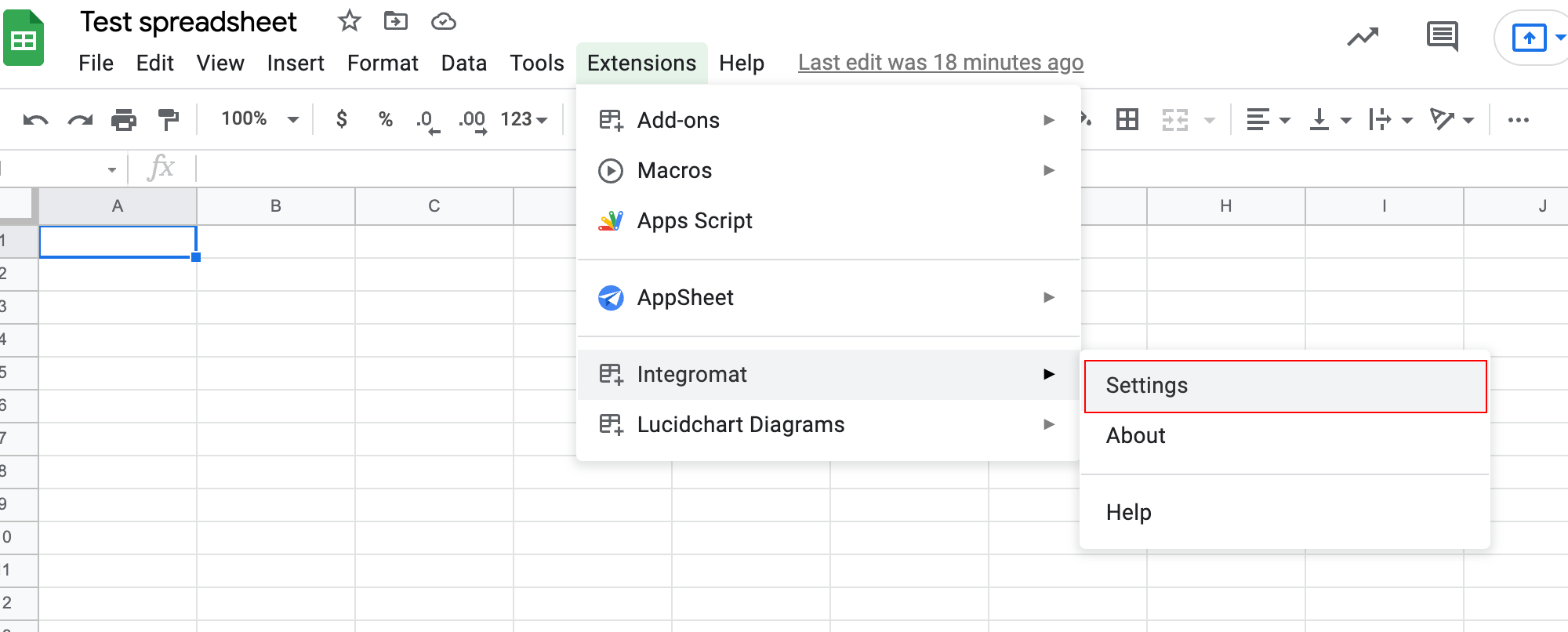
Open the Boost.space Integrator add-on settings.
-
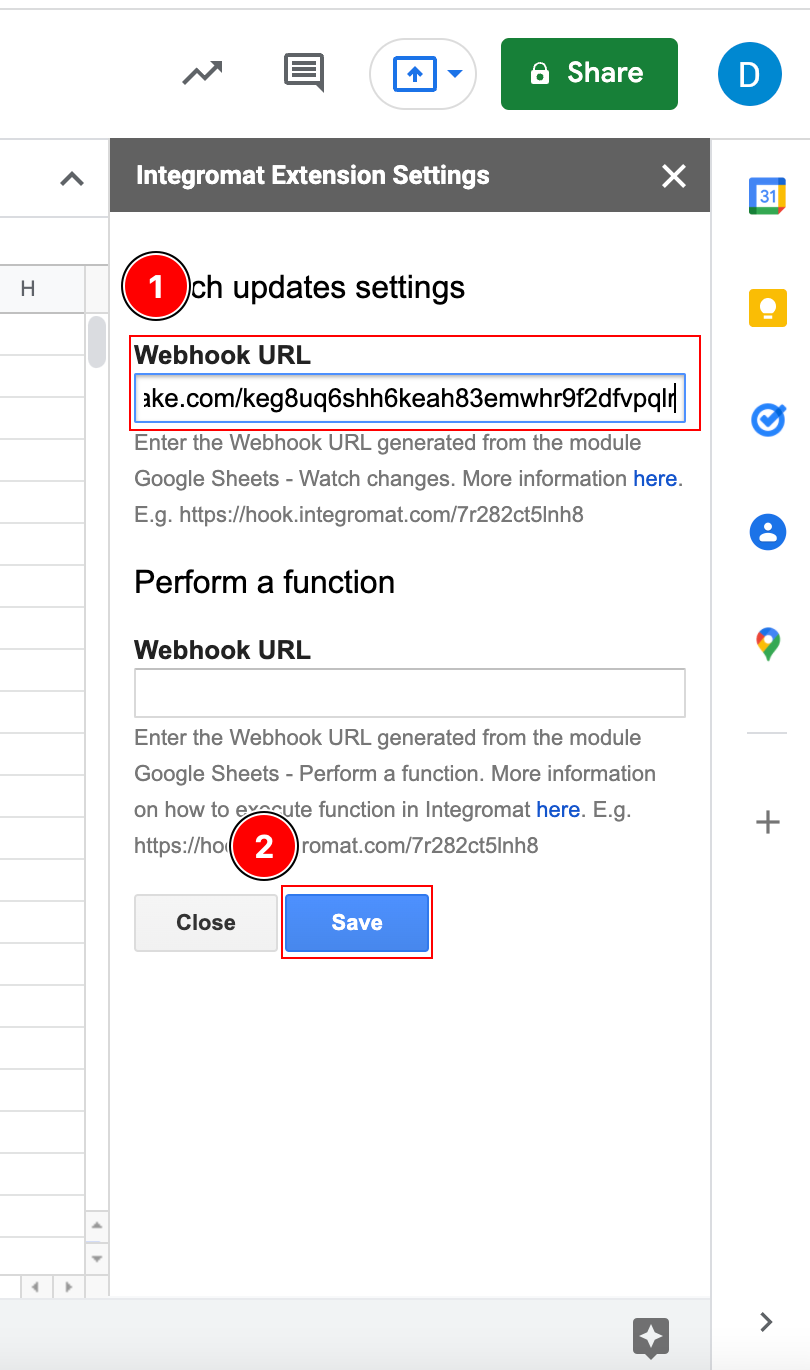
Paste the webhook URL you have copied in step 1 to the Webhook URL field in the Watch Updates settings section or Perform a FunctionFunctions you can use in Boost.space Integrator - create, update, delete, get, search. section, depending upon which module you are using.
-
Click Save.
You can find over 100 predefined Google Sheets sample templatesTemplates are predefined scenarios that you can expand and customize to create new scenarios. You can then share these with friends and colleagues. More here.
Retrieves values from every newly added row in the spreadsheet.
The module retrieves only new rows that have not been filled in before. The trigger will not process an overwritten row.
![[Tip]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/tip.png) |
Tip |
|---|---|
|
You can trigger a scenario in Boost.space Integrator using a custom button in Google Sheets. See here for more information. |
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Choose a Method |
Select a method to choose the spreadsheet whose rows you want to watch. |
|
Choose a Drive |
Select Google Drive, where you have the spreadsheet whose rows you want to watch. |
|
Spreadsheet ID |
Choose the Spreadsheet ID whose rows you want to watch. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select the spreadsheet that contains the sheet you want to watch. |
|
Table contains headers |
Select whether the spreadsheet contains the header row. If the Yesoption is selected, the module doesn’t retrieve the header row as output data, and variables in the output are then called by the headers. If the Nooption is selected, the module retrieves the first table row, and the output variables are called simply A, B, C, D, etc. |
|
Row with headers |
Enter the range of the header row, e.g., |
|
Value render option |
Formatted value The values in the reply will be calculated and formatted according to the cell’s formatting. Formatting is based on the spreadsheet’s locale, not the requesting user’s locale. For example, if Unformatted value The values will be calculated but not formatted in the reply. For example, if Formula The values will not be calculated. The reply will include the formulas. For example, if |
|
Date and time render option |
Serial number Instructs date, time, datetime, and duration fields to be outputted as doubles in “serial number” format, as popularized by Lotus 1-2-3. The whole number portion of the value (to the left of the decimal) counts the days since December 30th, 1899. The fractional portion (to the right of the decimal) counts the time as a fraction of the day. For example, January 1st, 1900 at noon would be 2.5. 2 because it’s 2 days after December 30th, 1899, and .5 because noon is half a day. February 1st, 1900 at 3 pm would be 33.625. This correctly treats the year 1900 as not a leap year. Formatted string Instructs date, time, datetime, and duration fields to be outputted as strings in their given number format (which depends on the spreadsheet’s locale). |
|
Limit |
Set the maximum number of results that Boost.space Integrator will work with during one execution cycleA cycle is the operation and commit/rollback phases of scenario execution. A scenario may have one or more cycles (one is the default).. |
![[Caution]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/caution.png) |
Caution |
|---|---|
|
If the worksheet contains a blank row, no rows after the blank row will be processed! |
This module watches for changes in all the cells of a spreadsheet. It means that when you update numerous cells in one row, one by one, Boost.space Integrator will then receive multiple updated events.
![[Note]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
The module only watches for changes made in the Google Sheets app by the userCan use the system on a limited basis based on the rights assigned by the admin. More. Script executions and API requests do not trigger this module. The module does not watch for newly added rows to the sheet. |
![[Tip]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/tip.png) |
Tip |
|---|---|
|
You can trigger a scenario in Boost.space Integrator using a custom button in Google Sheets. See here for more information. |
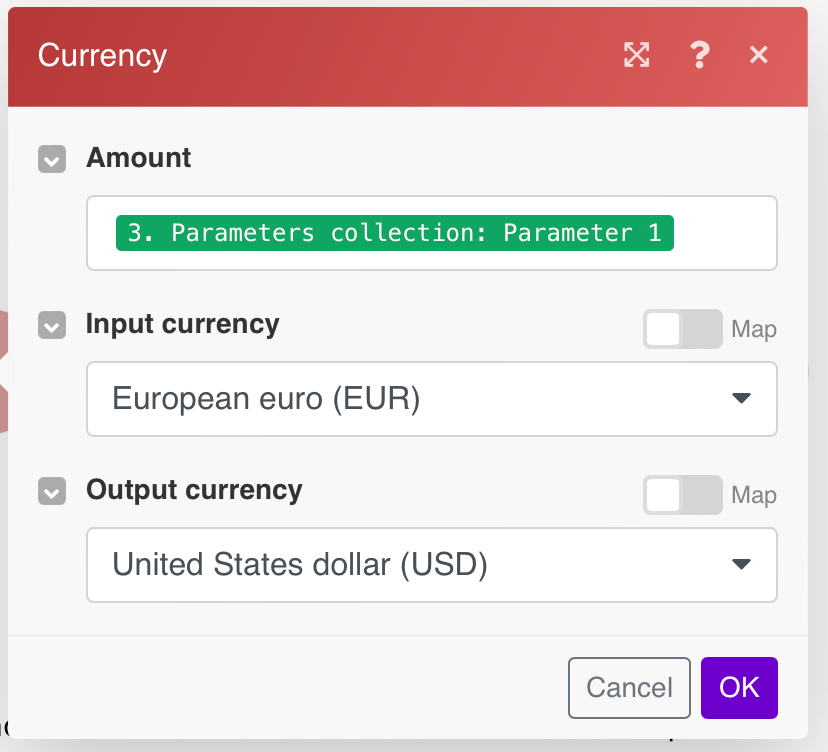
Boost.space Integrator allows you to use the custom functionCreate and execute custom JavaScript functions in your scenarios. MAKEin Google Sheets similarly to built-in functionsFunctions you can use in Boost.space Integrator - create, update, delete, get, search. like AVERAGE, SUM, etc. It allows you to perform the function in Boost.space Integrator and return the result back to the sheet. The function MAKE accepts as many parameters as you need.
|
Sample sheet |
The Total – EUR amount SUM will be converted, according to the current exchange rate, to the Total – USD amount and will be inserted into the desired field using Boost.space Integrator. 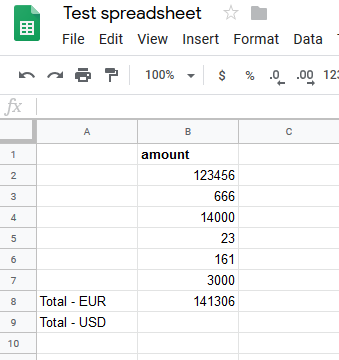 |
-
Create a scenario. Use the following modules:
-
Google Sheets > Perform a Function
-
Currency > Convert an Amount between Currencies
-
Google Sheets > Perform a Function – Responder
-
Google Sheets > Perform a Function
Generate a webhook and paste it into the Boost.space Integrator add-on in Google Sheets.
-
Currency > Convert an Amount between Currencies
Converts the mapped EUR amount to USD.
-
Google Sheets > Perform a Function – Responder
Inserts the converted amount into the sheet cell.
-
-
Run the scenario
-
Enter the MAKE function into the desired cell to load the converted amount.
When the user changes the amount, the MAKE function re-calculates the Total – USD according to the current exchange rate:
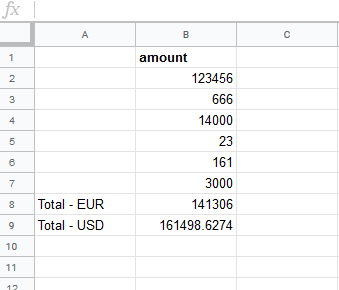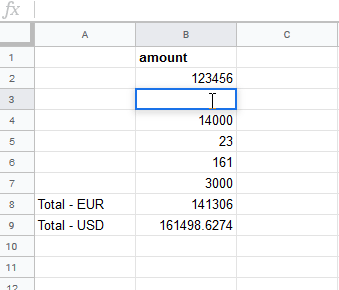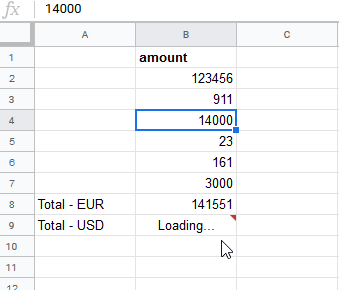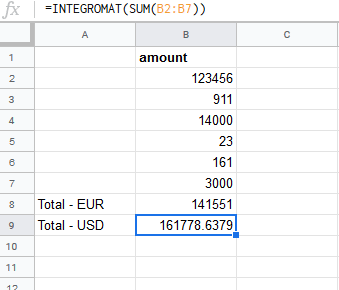
You can simply use the function like built-in functions in Google Sheet.
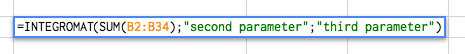
Create a new scenario with the following modules:
-
Perform a Function – the module receives the parameters passed to the function
-
Perform a Function – Responder – the module returns the result of the function execution back to the sheet
Adds a row to a sheet.
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Choose a Method |
Select an option to choose the spreadsheet in which you want to add a row. |
|
Choose a Drive |
Select Google Drive to choose the spreadsheet in which you want to add a row. |
|
Spreadsheet ID |
Enter the Spreadsheet ID in which you want to add a row. Alternatively, you can search the spreadsheet by clicking Search Spreadsheets. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select the Google spreadsheet. |
|
Sheet Name |
Enter a sheet name in which you want to add a row. |
|
Column range |
Select the column range that you want to work with. |
|
Unformatted |
Select or map whether to insert a row unformatted. |
|
Values |
Enter (map) the desired cells of the row you want to add. |
|
Value input option |
User entered The values will be parsed as if the user typed them into the UI. Numbers will remain numbers, but strings may be converted to numbers, dates, etc., following the same rules that are applied when entering text into a cell via the Google Sheets UI. Raw The values the user has entered will not be parsed and will be stored as-is. |
|
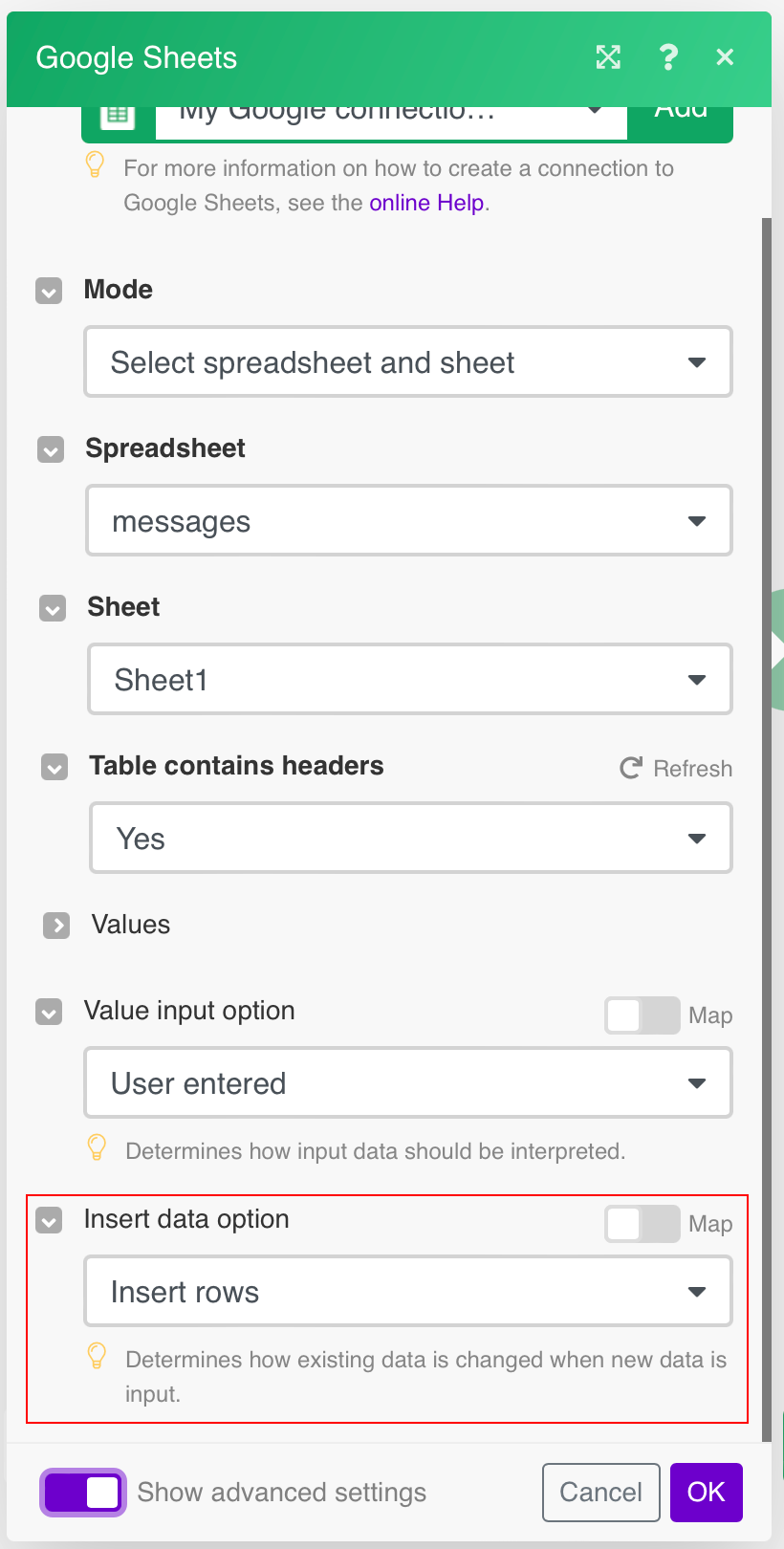
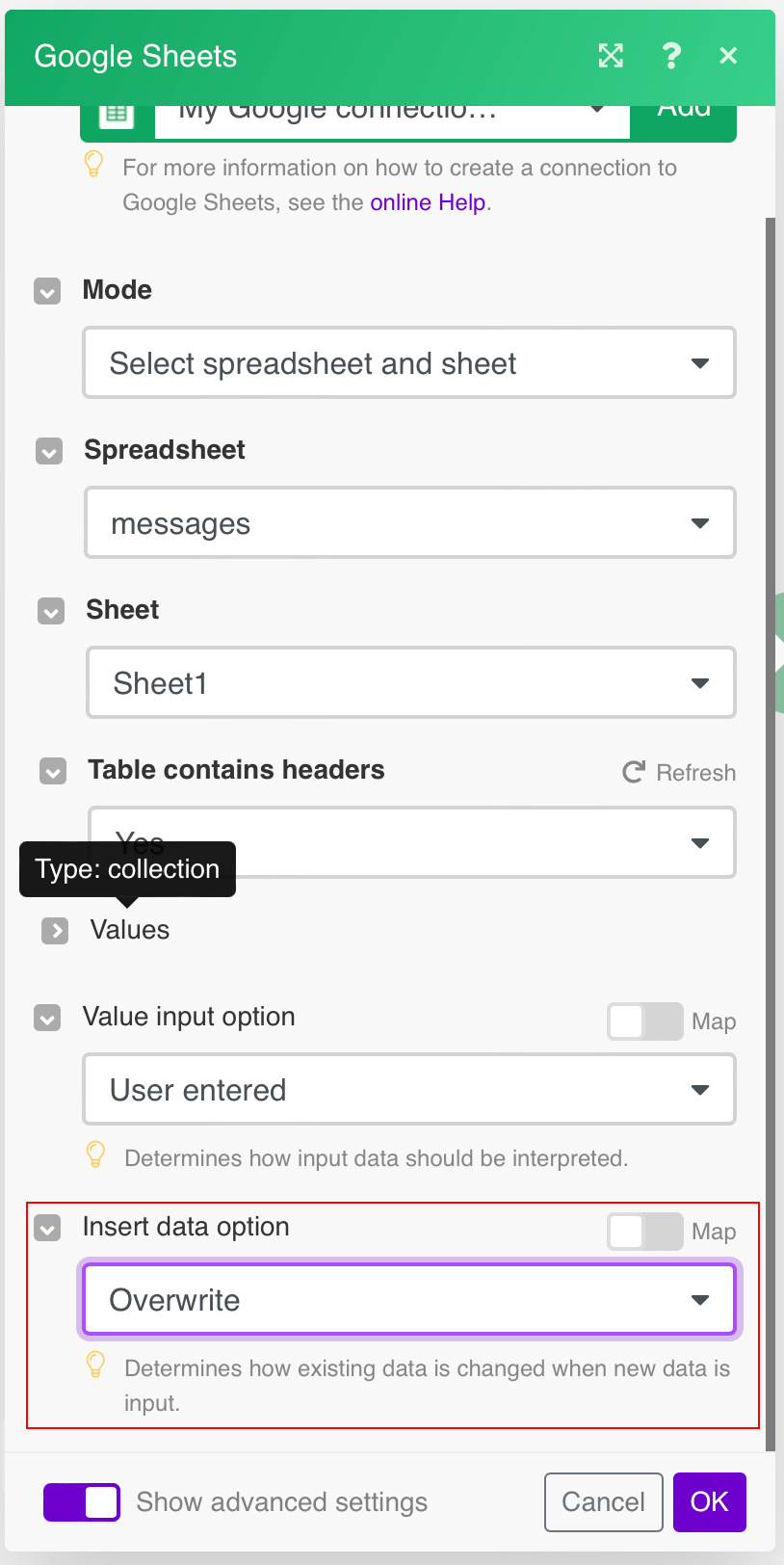
Insert data option |
Insert rows Rows are inserted for the new data. Example What happens when the Insert rows option is selected (the Add a Rowmodule is executed 3 times): 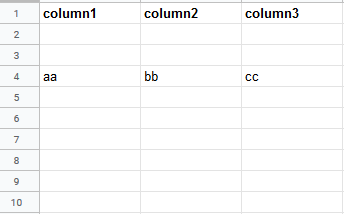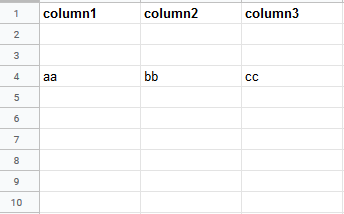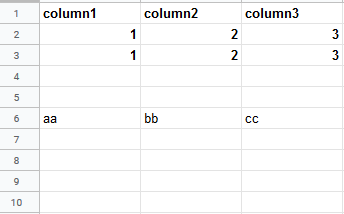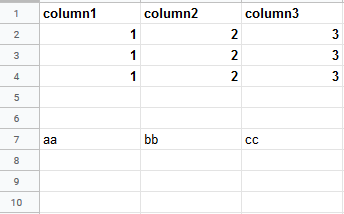 Overwrite The new data overwrites the existing data in the areas where it is written. (Note: adding data to the end of the sheet will still insert new rows or columns so the data can be written.) Example What happens when the Overwrite option is selected (the Add a Rowmodule is executed 3 times): 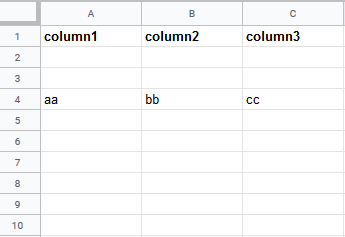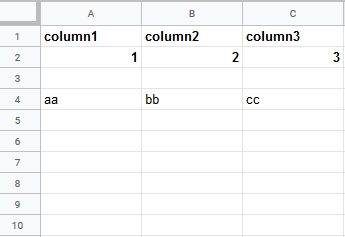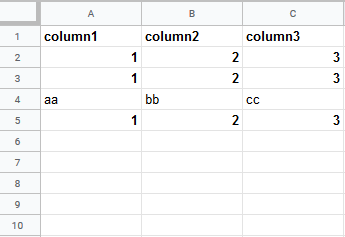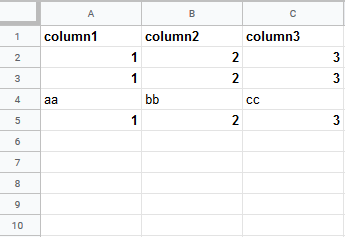 |
This module allows you to change the cell content in a selected row.
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Choose a Method |
Select an option to choose the spreadsheet whose rows you want to update. |
|
Choose a Drive |
Select Google Drive to choose the spreadsheet whose rows you want to update. |
|
Spreadsheet ID |
Enter the Spreadsheet ID whose rows you want to update. Alternatively, you can search the spreadsheet by clicking the Search Spreadsheets. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select the Google spreadsheet. |
|
Sheet |
Select the sheet you want to update a row in. |
|
Row number |
Enter the number of the row you want to update. |
|
Values |
Enter (map) the values in the desired cells of the row you want to change (update). |
|
Value input option |
User entered The values will be parsed as if the user typed them into the UI. Numbers will remain numbers, but strings may be converted to numbers, dates, etc. following the same rules that are applied when entering text into a cell via the Google Sheets UI. Raw The values the user has entered will not be parsed and will be stored as-is. |
Deletes values from a specified row.
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select the Google spreadsheet. |
|
Sheet |
Select the sheet you want to delete data from. |
|
Row number |
Enter the number of the row you want to delete, e.g. |
Deletes a specified row.
![[Note]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
To delete multiple rows based on filter criteria please see the Deleting Multiple Rows section. |
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select the Google spreadsheet. |
|
Sheet |
Select the sheet you want to delete a row from. |
|
Row number |
Enter the number of the row you want to delete, e.g. |
Retrieves a value from a selected cell.
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select the Google spreadsheet. |
|
Sheet |
Select the sheet that contains the cell you want to retrieve data from. |
|
Cell |
Enter the ID of the cell you want to retrieve data from, e.g. |
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select the Google spreadsheet. |
|
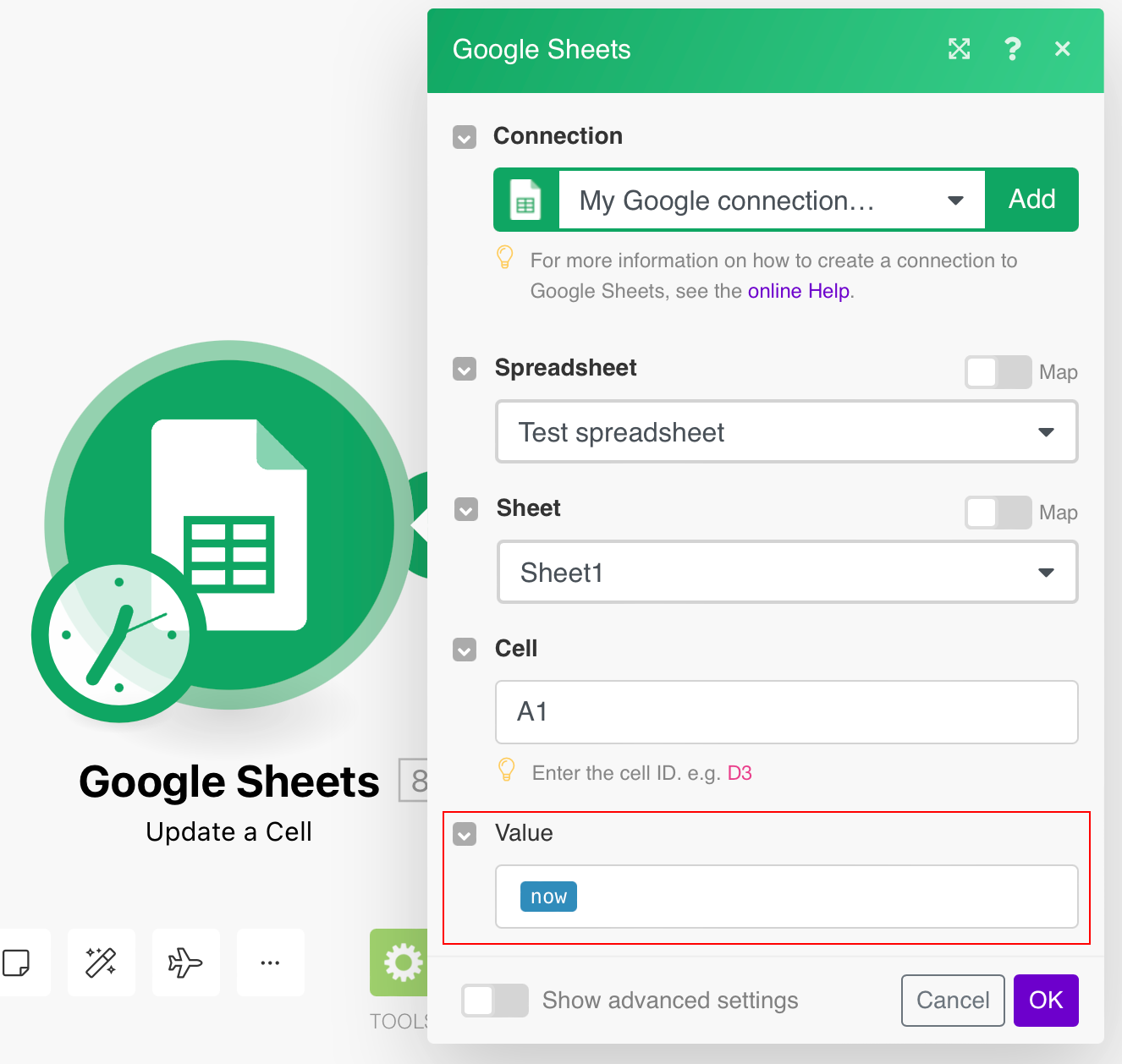
Cell |
Enter the ID of the cell you want to update, e.g. |
|
Value |
Enter the new value. |
|
Value input option |
User entered The values will be parsed as if the user typed them into the UI. Numbers will remain numbers, but strings may be converted to numbers, dates, etc., following the same rules that are applied when entering text into a cell via the Google Sheets UI. Raw The values the user has entered will not be parsed and will be stored as-is. |
Deletes a value from a specified cell.
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select the Google spreadsheet. |
|
Sheet |
Select the sheet you want to delete a cell from. |
|
Cell |
Enter the ID of the cell you want to delete, e.g. |
Creates a new sheet in a selected spreadsheet.
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select the Google spreadsheet. |
|
Properties |
Title Enter the name of the new sheet. Index Enter the sheet position. The default is |
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Title |
Enter the name of a new spreadsheet. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Locale |
The locale of the spreadsheet in one of the following formats: |
||||||||||||||||
|
Recalculation interval |
The amount of time to wait before volatile functions are recalculated: On change Volatile functions are updated upon every change. On change and every minute Volatile functions are updated upon every change and every minute. On change and hourly Volatile functions are updated upon every change and hourly. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Time zone |
Select the time zone of the spreadsheet. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Number format |
Select the default format of all cells in the spreadsheet.
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Sheets |
Add sheets to the new spreadsheet. |
This module is to be used together with the Perform a Function module.
|
Response type |
Select whether you insert text or a number into the sheet. |
|
Value |
Map the value from the previous module you want to insert into the sheet. |
Deletes a specified sheet from a spreadsheet.
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select or map the Google spreadsheet that contains the sheet you want to delete. |
|
Sheet |
Select or map the sheet you want to delete. |
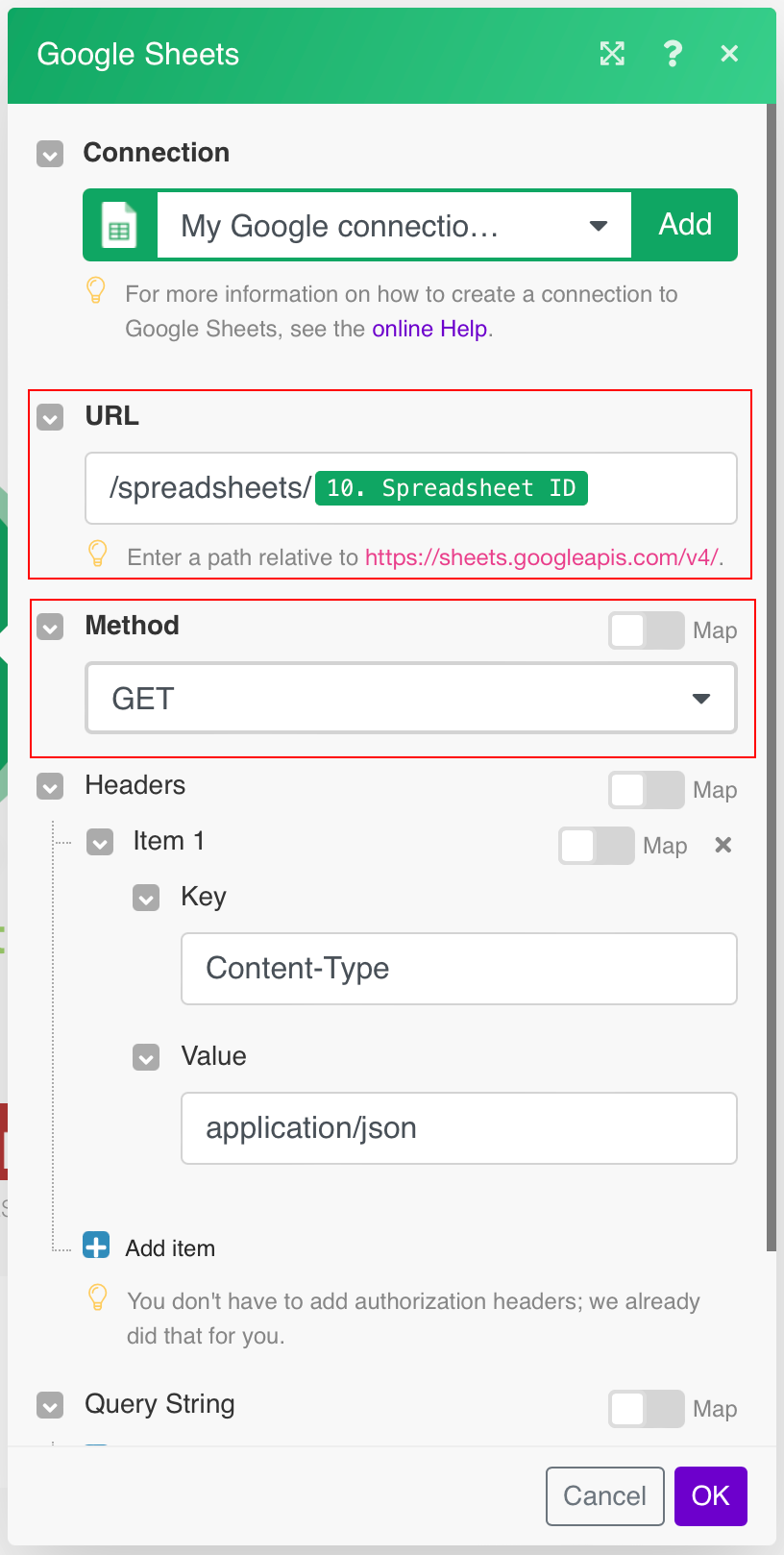
Allows you to perform a custom API call.
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|||
|
URL |
Enter a path relative to For example:
|
|||
|
Method |
Select the HTTP method you want to use:
|
|||
|
Headers |
Enter the desired request headers. You don’t have to add authorization headers; we already did that for you. |
|||
|
Query String |
Enter the request query string. |
|||
|
Body |
Enter the body content for your API call. |
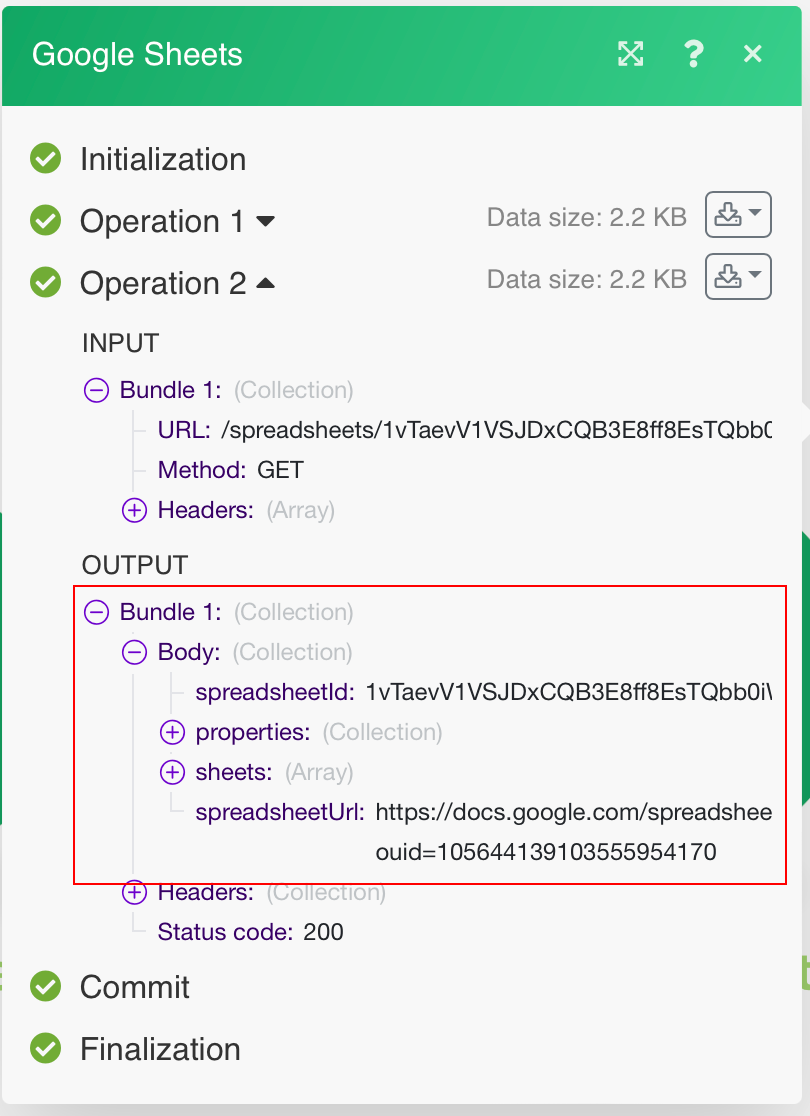
The following API call returns specified spreadsheet details.
URL:
/spreadsheets/{{spreadsheetID}}
Method:
GET
The result can be found in the module’s Output under BundleA bundle is a chunk of data and the basic unit for use with modules. A bundle consists of items, similar to how a bag may contain separate, individual items. More > Body:
Creates a new spreadsheet from a templateTemplates are predefined scenarios that you can expand and customize to create new scenarios. You can then share these with friends and colleagues. More sheet.
|
Connection |
|
|
Enter a Template Spreadsheet ID |
Select or map the Template Spreadsheet ID from which you want to create the spreadsheet. |
|
Choose a Drive |
Select or map the drive where you want to create the spreadsheet. |
|
Template Spreadsheet ID |
Select the template from which you want to create the spreadsheet. If the spreadsheet contains tags like Your file MUST contain at least one tag for this module to work. |
|
Title |
Enter a name for the spreadsheet. |
|
New Drive Location |
Select or map the drive to store the new spreadsheet. |
|
New Document’s Location |
Select or map the folder, where the new spreadsheet should be placed. |
Copies a sheet to another spreadsheet.
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to your Google Spreadsheets account. |
|
Choose a Method |
Select or map the option to choose the spreadsheet that you want to copy. |
|
Choose a Drive |
Select or map the drive location where the spreadsheet that you want to copy is located. |
|
Spreadsheet ID |
Select or map the Spreadsheet ID you want to copy. |
|
Destination Drive Location |
Select or map the drive location where you want to store the copied spreadsheet. |
|
Destination Spreadsheet ID |
Select or map the copied Spreadsheet ID. |
Clears a specified range of values from a spreadsheet.
|
Connection |
|
|
Enter a Spreadsheet ID and Sheet Name |
Select an option to choose the spreadsheet and sheet name whose value you want to clear.
|
|
Spreadsheet ID |
Enter the Spreadsheet ID from which you want to clear the values. |
|
Sheet Name |
Enter a sheet name from which you want to clear the values. |
|
Range |
Enter the range you want to get. For example, A1:D25. |
Creates a new conditional format rule at the given index. All subsequent rules indexes are incremented.
|
Connection |
|
|
Enter a Spreadsheet and Sheet ID |
Select an option to choose the spreadsheet and sheet name to which you want to create a format rule.
|
|
Spreadsheet ID |
Enter the Spreadsheet ID to which you want to create the conditional format rule. |
|
Sheet ID |
Enter the Sheet ID to which you want to create the conditional format rule. |
|
Range |
Enter the range of rows and columns to which you want to apply the conditional rule format. For example, A1:D25. |
|
Index |
The zero-based index where the rule should be inserted. |
|
Format Rule |
Select or map the rule for the conditional format rule. |
|
Condition |
Select or map the condition and enter the value for the format rule. For more information, see the boolean and gradient conditions. |
|
Cell Format |
Select or map the cell background color. |
|
Text Format |
Set the text format such as foreground color, bold, italic or strikethrough. |
Deletes a conditional format rule at the given index. All subsequent rule indexes are decremented.
|
Connection |
|
|
Enter a Spreadsheet and Sheet ID |
Select an option to choose the spreadsheet and sheet name to which you want to create a format rule.
|
|
Spreadsheet ID |
Enter the Spreadsheet ID whose conditional format rule you want to delete. |
|
Sheet ID |
Enter the Sheet ID whose conditional format rule you want to delete. |
|
Index |
The zero-based index of the rule to be deleted |
Searches rows using the filter options.
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select the Google spreadsheet. |
|
Sheet |
Select the sheet you want to search the rows in. |
|
Table contains headers |
Select whether the spreadsheet contains the header row. If the Yesoption is selected, the module doesn’t retrieve the header row as output data and variables in the output are then called by the headers. If the Nooption is selected, the module also retrieves the first table row, and variables in the output are then called simply A, B, C, D, etc. |
|
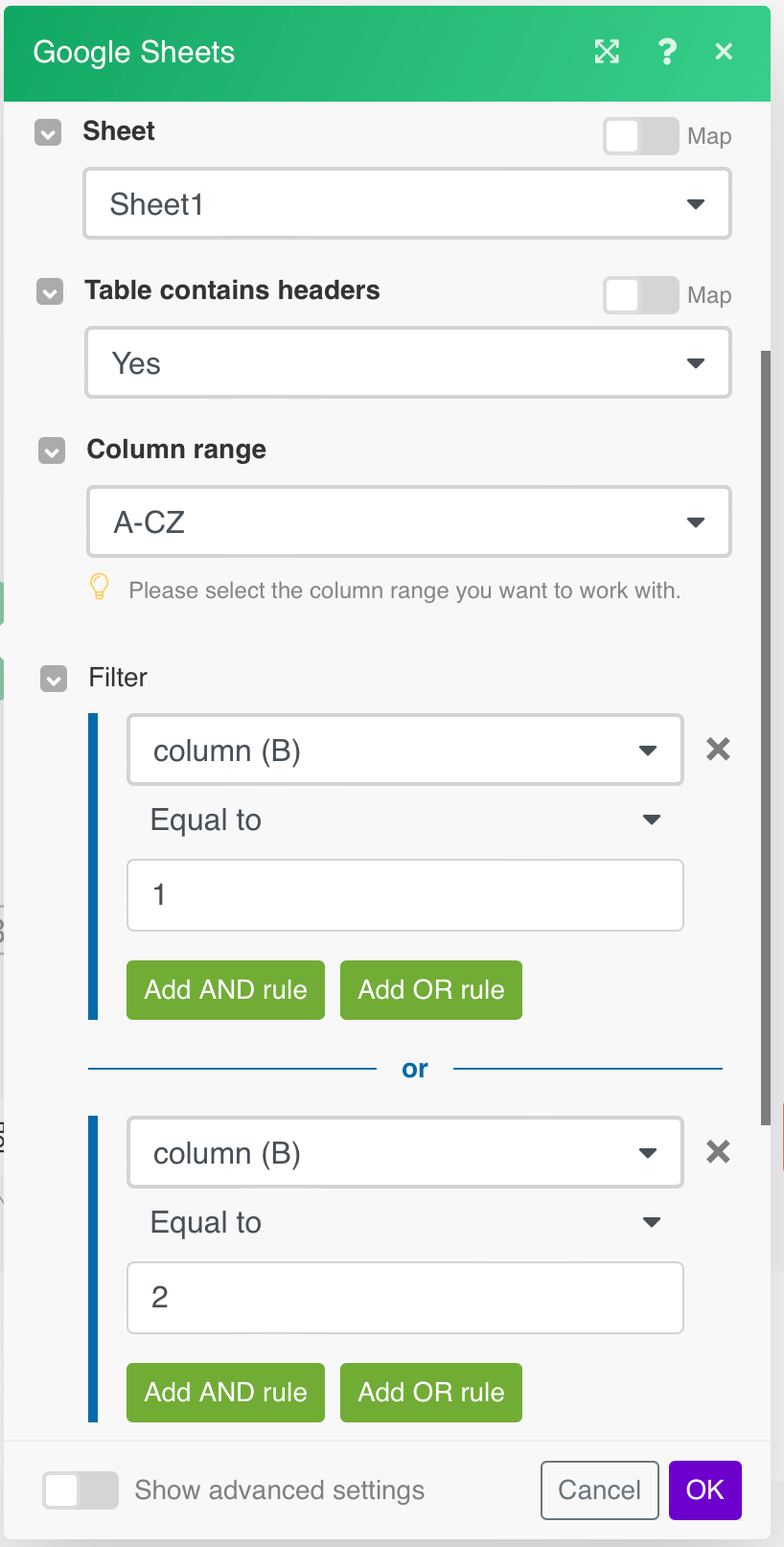
Filter |
Set the filter for the row to be searched by. Set filter values. You can also use logical operators, AND/OR in order to specify your selection. Example: In the following dialog, the row which contains the number 1 or 2 in the “column2” column will be searched. |
|
Field Type |
Select or map the field type to search the rows that match the specified type:
|
|
Formatted value The values in the reply will be calculated and formatted according to the cell’s formatting. Formatting is based on the spreadsheet’s locale, not the requesting user’s locale. For example, if Unformatted value The values will be calculated, but not formatted in the reply. For example, if Formula The values will not be calculated. The reply will include the formulas. For example, if |
|
|
Date and time render option |
Serial number Instructs date, time, datetime, and duration fields to be output as doubles in “serial number” format, as popularized by Lotus 1-2-3. The whole number portion of the value (to the left of the decimal) counts the days since December 30th 1899. The fractional portion (to the right of the decimal) counts the time as a fraction of the day. For example, January 1st 1900 at noon would be 2.5. 2 because it’s 2 days after December 30th 1899, and .5 because noon is half a day. February 1st 1900 at 3 pm would be 33.625. This correctly treats the year 1900 as not a leap year. Formatted string Instructs date, time, datetime, and duration fields to be outputted as strings in their given number format (which is dependent on the spreadsheet’s locale). |
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select the Google spreadsheet. |
|
Sheet |
Select the sheet you want to search the rows in. |
|
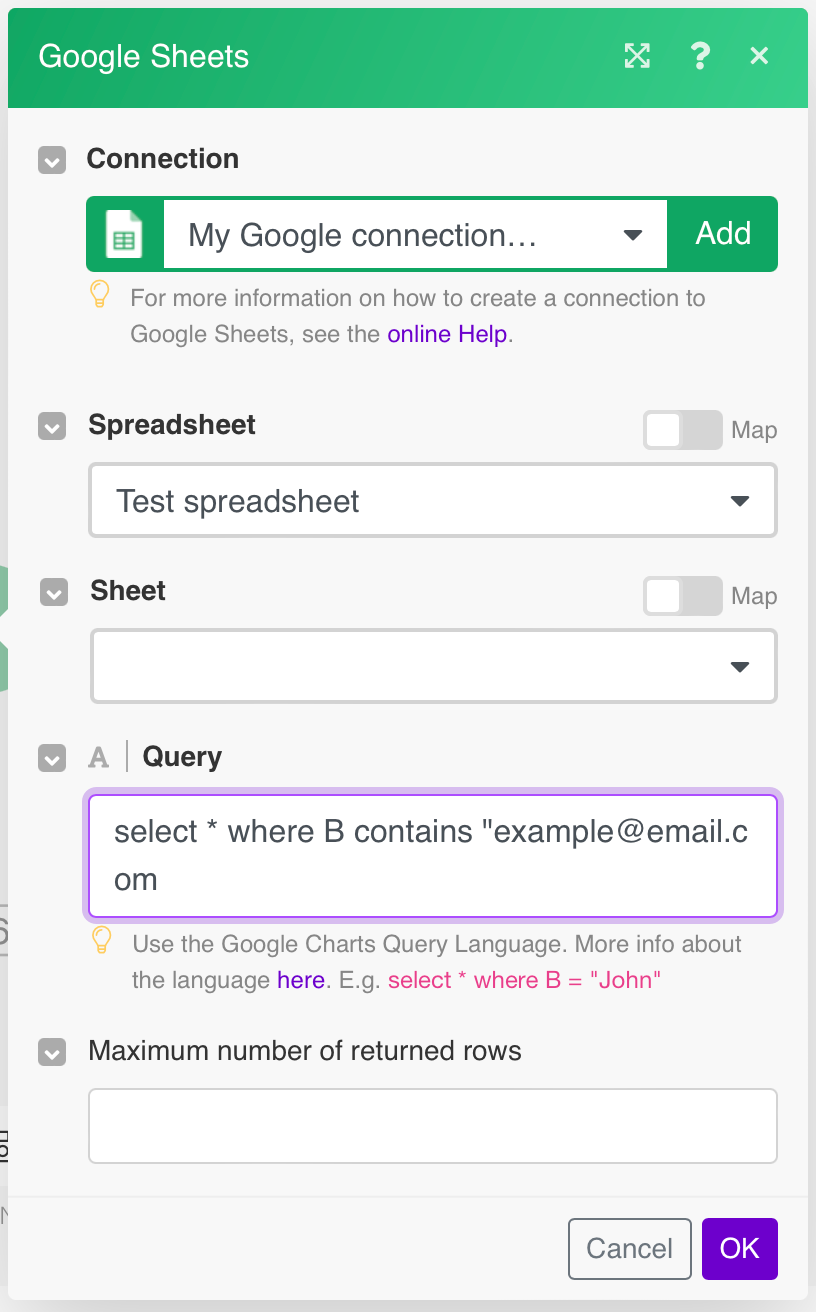
Query |
Searches rows using Google Charts Query Language. The language is similar to SQL and it is possible to make complex queries. Unfortunately, the response doesn’t contain IDs of returned rows. Due to Google Charts, the service is intended for data visualization where the row numbers aren’t needed. You can find more information about the query language in the documentation. |
Retrieves range content.
|
Connection |
Establish a connection to the spreadsheet using your Google account. |
|
Spreadsheet |
Select the Google spreadsheet. |
|
Sheet |
Select the sheet you want to get the range content from. |
|
Range |
Enter the range you want to get, e.g. |
|
Table contains headers |
Row with headers Enter the range of the table headers, e.g. |
|
Value render option |
Formatted value The values in the reply will be calculated and formatted according to the cell’s formatting. Formatting is based on the spreadsheet’s locale, not the requesting user’s locale. For example, if Unformatted value The values will be calculated, but not formatted in the reply. For example, if Formula The values will not be calculated. The reply will include the formulas. For example, if |
|
Date and render option |
Serial number Instructs date, time, datetime, and duration fields to be output as doubles in “serial number” format, as popularized by Lotus 1-2-3. The whole number portion of the value (to the left of the decimal) counts the days since December 30th 1899. The fractional portion (to the right of the decimal) counts the time as a fraction of the day. For example, January 1st 1900 at noon would be 2.5. 2 because it’s 2 days after December 30th 1899, and .5 because noon is half a day. February 1st 1900 at 3 pm would be 33.625. This correctly treats the year 1900 as not a leap year. Formatted string Instructs date, time, datetime, and duration fields to be outputted as strings in their given number format (which is dependent on the spreadsheet’s locale). |
If the errorService is unavailable due to a failure, a service responds with unexpected data or the validation of input data fails. More 429: RESOURCE_EXHAUSTEDoccurs, you have exceeded the API rate limit.
The Google Sheets API has a limit of 500 requests per 100 seconds per project, and 100 requests per 100 seconds per user. Limits for reads and writes are tracked separately. There is no daily usage limit.
See more details at developers.google.com/sheets/api/limits.
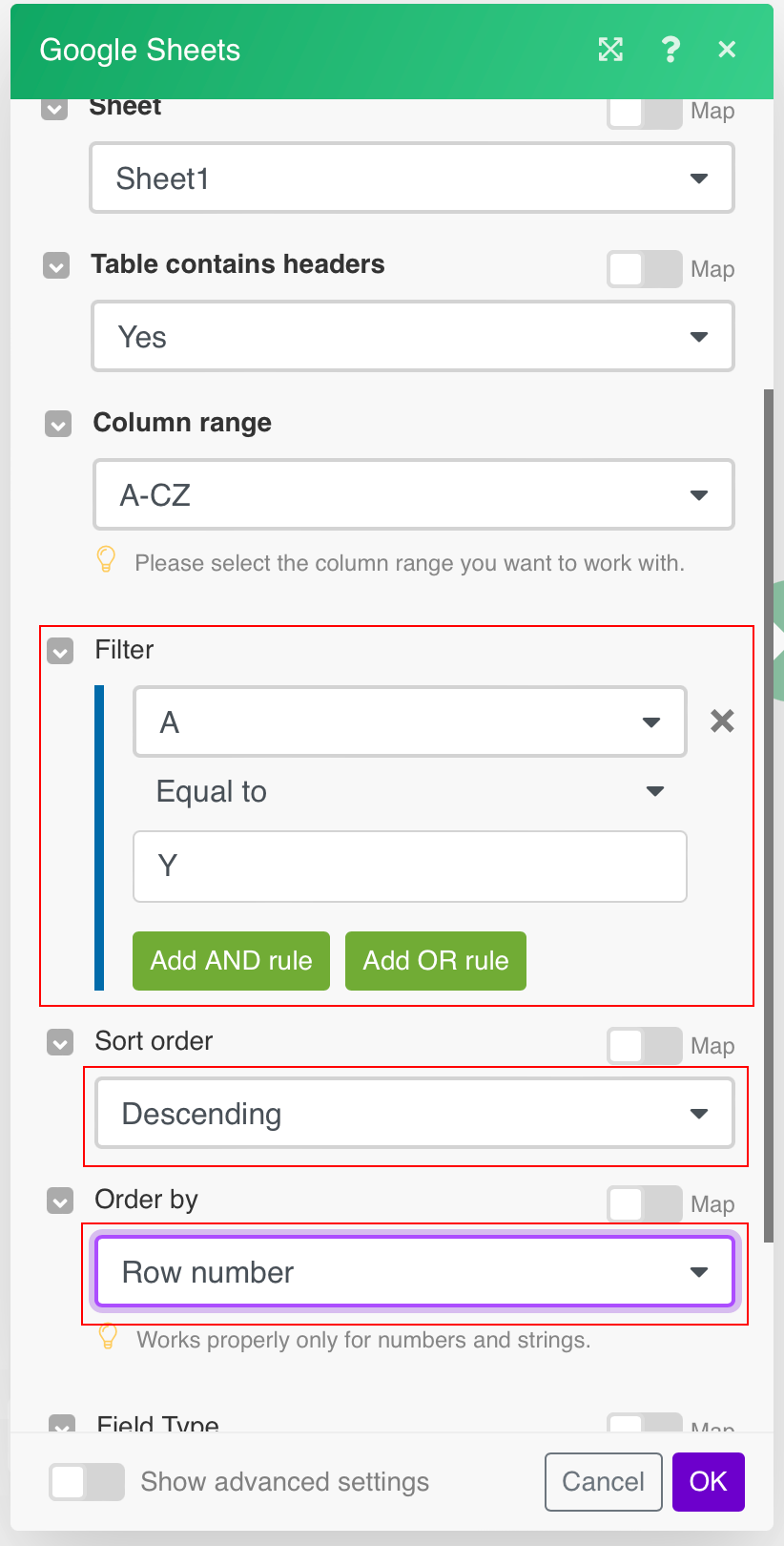
To delete multiple rows based on filter criteria use the Search Rows module linked to the Delete a Row module as on the following example:
-
1. Add the Search Rows module and Delete a Row module to the scenario.

-
Let’s assume that you have a table where you need to delete all rows where column A equals to Y.
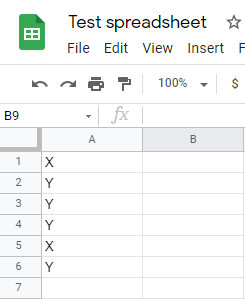
-
Open Search Rows module settings and set the fields as follows:
![[Caution]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/caution.png)
Caution Make sure that Sort order and Order by fields are set as above, otherwise, values will not be deleted correctly from the table!
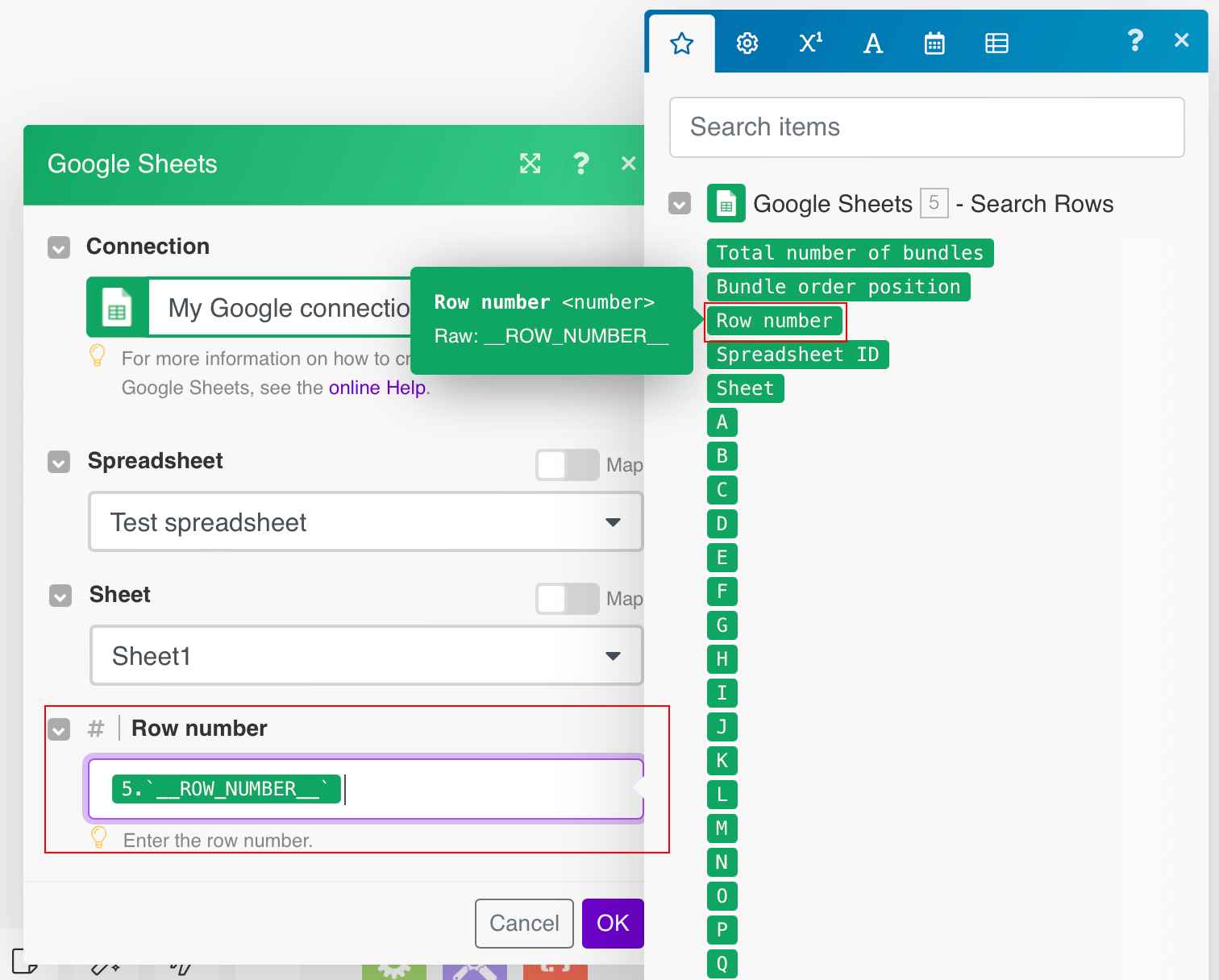
-
Add the Delete a Row module to the scenario and connect it to the Search Row module.
-
Map the Row number itemItems are rows in records (order/request/invoice/purchase...) from the Search Rows module to the Delete a Row module’s Row numberfield.
-
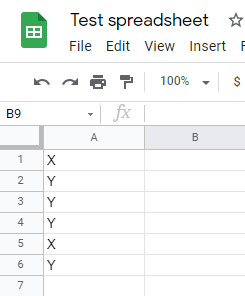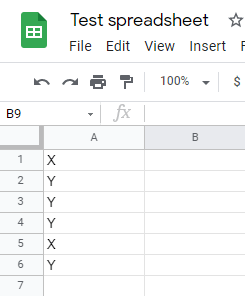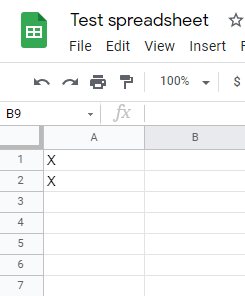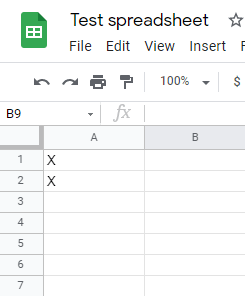
Run the scenario to delete values that match the filter criteria from the sheet.
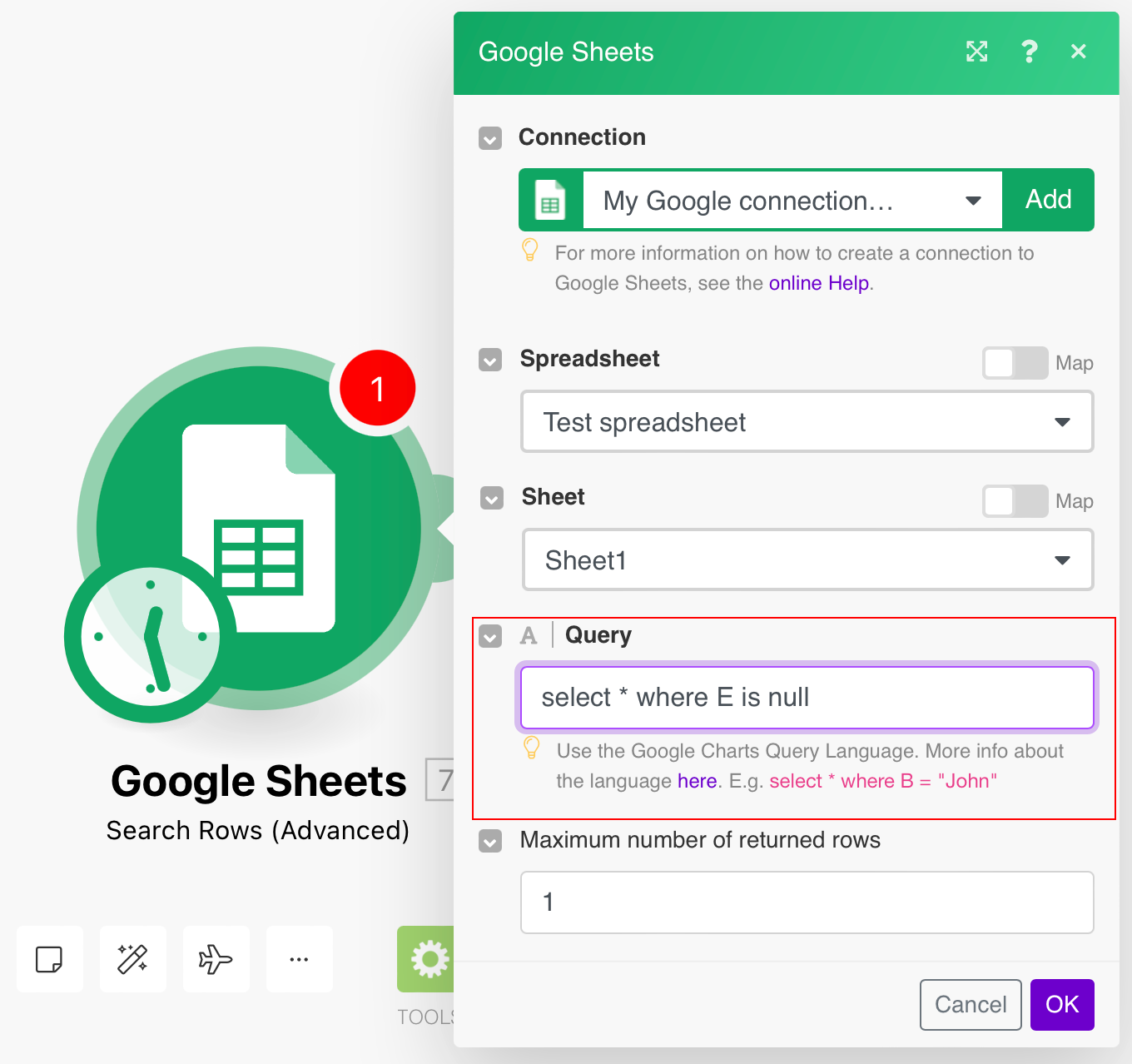
Use the Search Rows (Advanced) module & use this formula to get empty columns.
select * where E is nullHere “E” is the column & “is null” is the condition. You can create a more advanced query using Google Query Lang
-
In Boost.space Integrator, insert the Webhook > Custom webhooksA webhook is a way for an app to send real-time information to a specific URL in response to certain events or triggers. module/trigger into the scenario and configure it (see Webhooks).
-
Copy the webhook’s URL.
-
Execute the scenario.
-
In Google Sheets, choose Insert > Drawing… from the main menu bar.
-
Click the Text box icon:
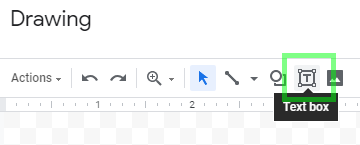
-
Design a button and click Save and Close in the top-right corner:
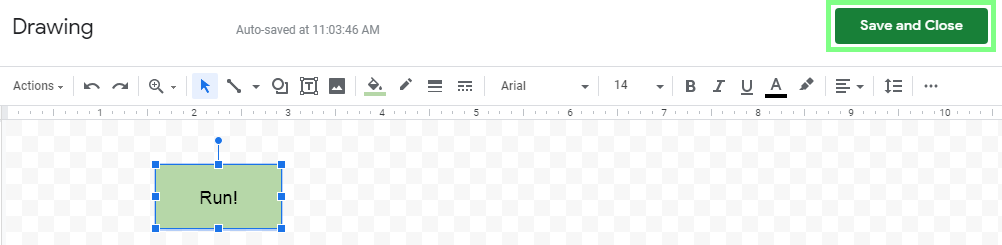
-
The button will be placed in your worksheet. Click the three vertical dots in the button’s top-right corner:

-
Choose Assign script… from the menu.
-
Enter the name of your script (function). For example,
runscenarioand click OK: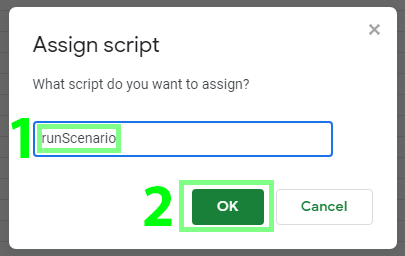
-
Choose Tools > Script editor from the main menu bar.
-
Insert the following code:
-
The name of the function must correspond to the name you specified in step 9.
-
Replace the
https://hook.make.com/xxx...xxxURL with the webhook’s URL you copied in step 2.function runScenario() { UrlFetchApp.fetch("https://hook.make.com/xxx...xxx"); }
-
-
Press Ctrl+S to save the script file, enter a project name, and click OK.
-
Switch back to Google Sheets and click your new button.
-
Grant the required authorization to the script:
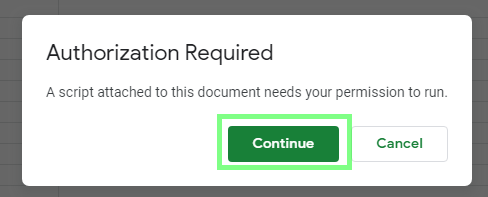
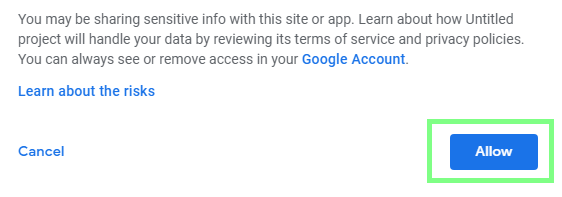
-
In Boost.space Integrator, verify that the scenario has successfully executed.
If you store a Date value in a spreadsheet without any formatting,
it will appear as text in ISO 8601 format in the spreadsheet. However, Google Sheets formulas or functions that work with dates do not understand this text. E.g. formula =A1+10 will display the following error:
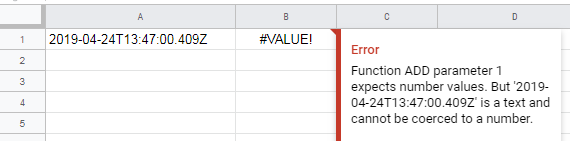
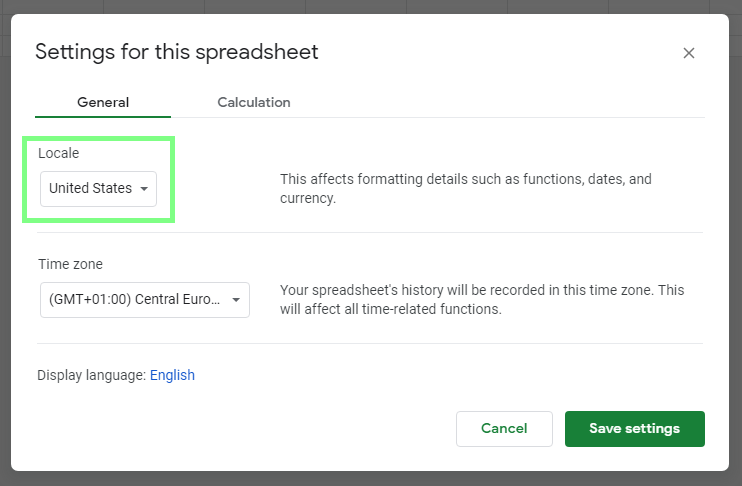
To help the GS to understand the date, format it with the formatDate(.) function. The correct format passed to the function as the second argument depends on the spreadsheet’s locale settings. Choose File ▶ Spreadsheet settings from the main menu to verify/set the locale:
Once you have verified/set the proper locale, determine the corresponding date and time format by choosing Format ▶ Number from the main menu. The format is displayed next to the Date time menu item:
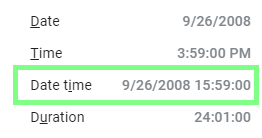
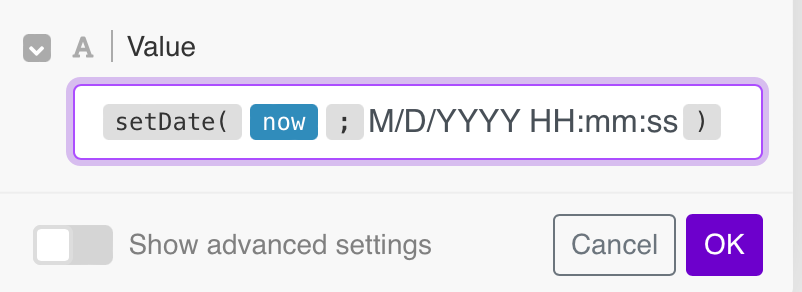
The following example shows the use of M/D/YYYY HH:mm:ss format for the United States locale:
If you miss a built-in function but it is featured by Google Sheets, you may exploit it.
When getting an image from Google Sheets, first make sure you enter the image as a formula. For example:=IMAGE("https://i.ytimg.com/vi/MPV2METPeJU/maxresdefault.jpg") making use of the =IMAGE(…)
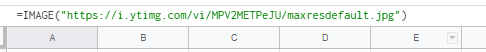
After you have done so, open the Google Sheets module (e.g. Watch Rows, Search Rows, Get a Cell) and select the Show advanced settings. Then select the Formula option in the Value render optionfield.
The output will be as shown below:
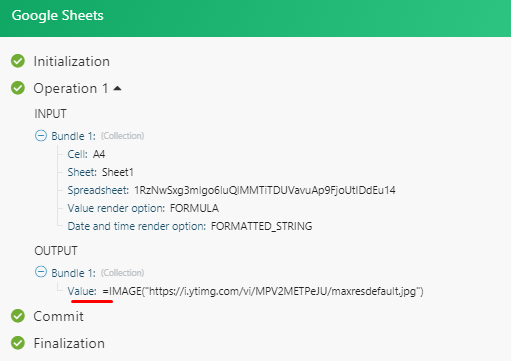
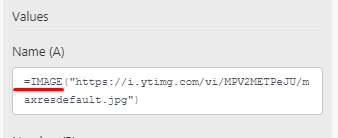
Then you can extract the URL using the replace function. The output will be just the URL.To be able to post an image, make sure to enter the =IMAGE(...) formula that will be used in the cell and then enter the Image URL address.

![[Important]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/important.png)