In this section, you will learn how a scenarioA specific connection between applications in which data can be transferred. Two types of scenarios: active/inactive. More executes and how data flows through a scenario. It will also show you where you can find information about your processed data and how to read it.
Once a scenario is set-up correctly and activated, it will execute according to its defined schedule.
The scenario begins with the first module responding to an event it has been set to watch for. If it returns any bundles (data), the bundles are then passed on to the next moduleThe module is an application or tool within the Boost.space system. The entire system is built on this concept of modularity. (module - Contacts) More and the scenario continues. If it does not return any modulesThe module is an application or tool within the Boost.space system. The entire system is built on this concept of modularity. (module - Contacts) More, the scenario does not continue and ends after the first module. In the case where there are returned bundles after the first module, the bundles will then go through each proceeding module one-by-one. If the bundles are processed correctly throughout all of the modules, the scenario is then marked as Successful.
The example below shows how Boost.spaceCentralization and synchronization platform, where you can organize and manage your data. More IntegratorPart of the Boost.space system, where you can create your connections and automate your processes. More connects three modules in a scenario. It explains how Boost.space Integrator downloads photos from Facebook, converts them to another format, and sends them to a selected Dropbox folder.
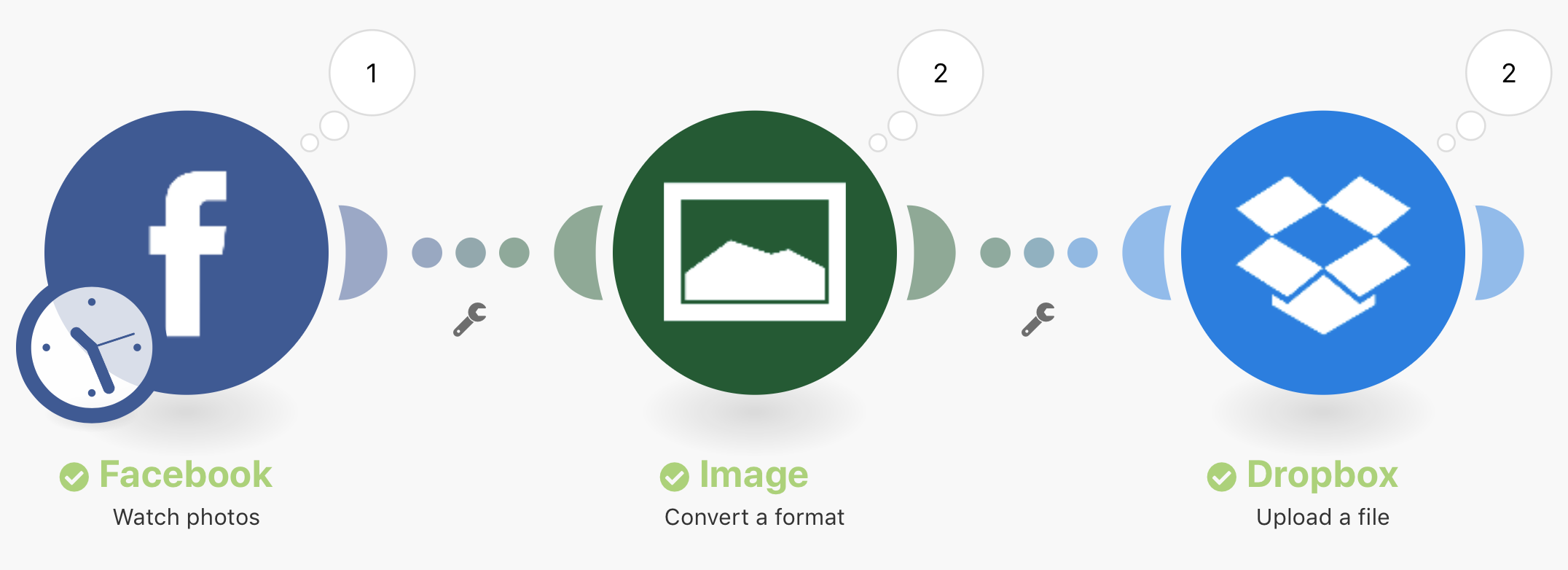
When the scenario begins, the first step is to watch for bundles. In this case, it is to watch for photos on Facebook. If it does not return a bundleA bundle is a chunk of data and the basic unit for use with modules. A bundle consists of items, similar to how a bag may contain separate, individual items. More (a photo), the processing of the scenario does not continue and ends after the first module.
If a bundle is returned, the bundle then passes through the rest of the scenario. The bundle is first recieved through the Watch photos module, then it goes through the Convert a format module for the Image app, and then goes through the Upload a file module for Dropbox to reach its final destination, the Dropbox folder.
It is also important to note that if Facebook returns multiple bundles, for example two bundles, the processing of the latter bundle will not start until the first bundle is converted and uploaded to Dropbox.
For each module, the bundle goes through a 4 step process before going on to the next module or reaching its final destination. The 4 step process is Initalization, OperationAn operation is a task performed by module. More, Commit/Rollback, and Finalization. This is called transaction processing and it helps to explain how data was processed in a module.
Once a scenario run is complete, each module displays an icon showing the number of operations performed. Clicking this icon will display the detailed information about the processed bundles, in the format described above. You can see which modules settings were used and which bundles were returned by which module.
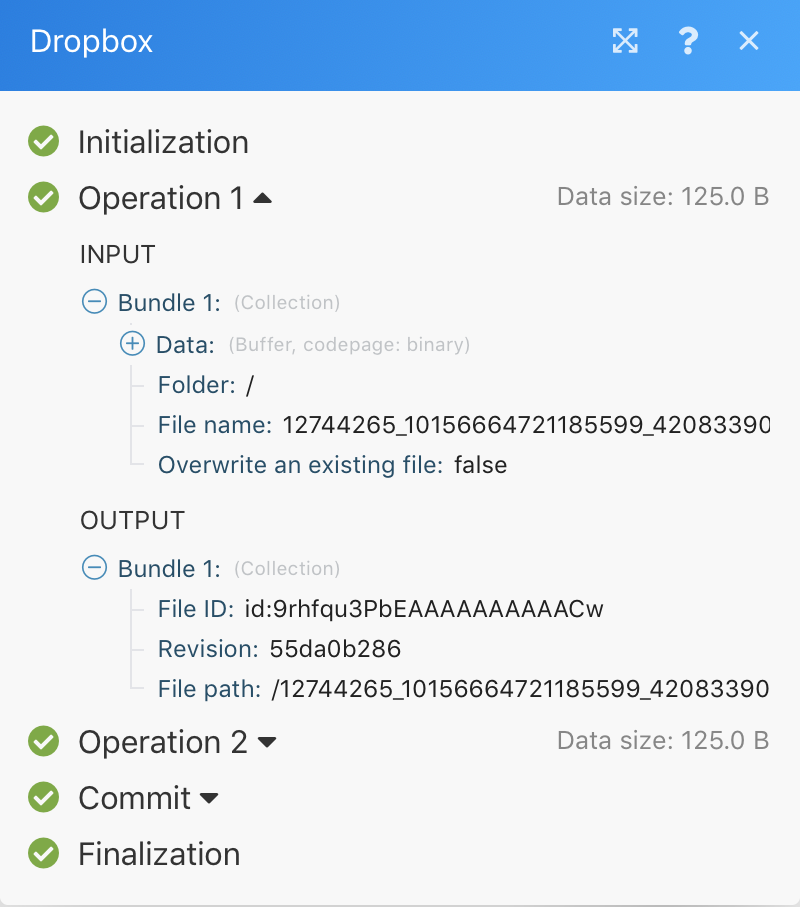
The picture beside illustrates the processing of the last module used in the scenario above, the Dropbox module, Upload a file.
The module received the following input information:
-
Converted image
-
Selected folder where the image shall be uploaded to
-
Original name of the Facebook image
After processing, the module returned this output information:
-
Image ID assigned by Dropbox
-
Full path where in Dropbox Boost.space Integrator uploaded the file
The above information is captured for each bundle separately, as marked by the drop down boxes Operation 1 and Operation 2 in the image.
An error may occur during the scenario run. For example, if you delete the Dropbox folder that you have set as the target folder in the module setting, the scenario will terminate with an error message. For more information on this and to learn how to handle errorsService is unavailable due to a failure, a service responds with unexpected data or the validation of input data fails. More, please see the Error processing help guide.
